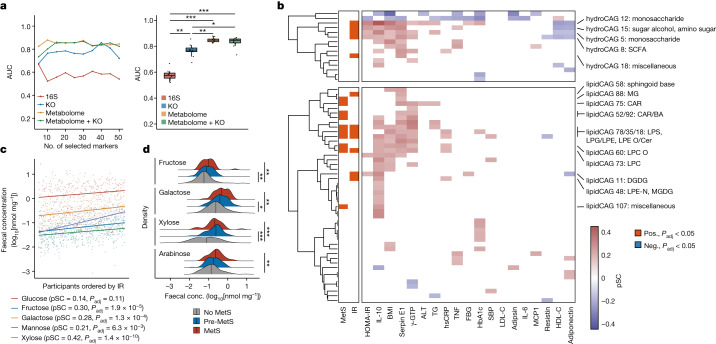
Fig. 1. Faecal carbohydrate metabolites are distinctly altered in IR.
a, Left, the AUC of random forest classifiers was used to predict IR based on genus-level 16S (n = 282), metagenome at the KEGG orthologue (KO) level (n = 266), faecal metabolome and metagenome (KEGG orthologue) + faecal metabolome (n = 266) data. The number of featured markers selected from the datasets increases along the x axis. Right, the box plots show the AUC obtained by selected features. Each dot represents an AUC value of a random-forest classifier using a given number of selected features as predictor variables. b, CAGs of faecal hydrophilic metabolites (hydroCAG, top) and lipid metabolites (lipidCAG, bottom), and clinical phenotypes and markers (n = 282). The two-column heat map on the left represents the associations with the main clinical phenotypes (IR and MetS) analysed using rank-based linear regression, whereas the main heat map shows the partial Spearman’s correlations (pSC) adjusted by age and sex with representative metabolic markers. Only the CAGs with adjusted P (Padj) < 0.05 are coloured. The category names for CAGs were determined on the basis of the most abundant metabolites in the CAGs. Further details are provided in Supplementary Tables 3–8. FBG, fasting blood glucose; neg., negative; pos., positive. The lipid abbreviations are defined in Supplementary Table 27. c, pSC between HOMA-IR and faecal levels of monosaccharides. The coefficients (pSC) and Padj values are described (n = 282). d, Faecal levels of monosaccharides in MetS (n = 306). For a, the box plots indicate the median (centre line), upper and lower quartiles (box limits), and upper and lower extremes except for outliers (whiskers). conc., concentration. For c, the density plots indicate median and distribution. For a and d, statistical analysis was performed using Kruskal–Wallis tests followed by Dunn’s test (a) and rank-based linear regression adjusted by age and sex (d); *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. See the Source Data (a) and Supplementary Table 5 (d) for exact P values.