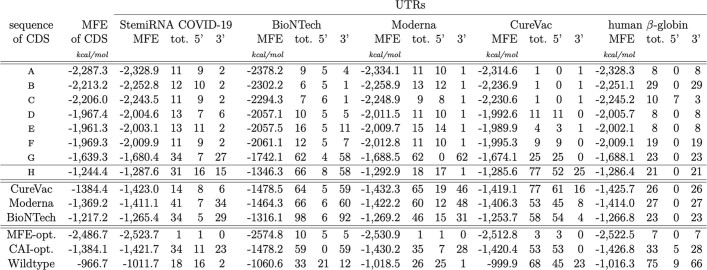
Extended Data Table 1.
The LinearDesign-generated coding-region sequences, due to more secondary structures within the coding region, are less likely to form base pairs with or interfere with the structures of the UTRs
Here we show the numbers of predicted base pairs between UTRs and the coding regions of SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein. We used 5 different UTRs: StemiRNA COVID-19 UTRs used in wet lab experiments, BNT-162b2 (BioNTech) UTRs, mRNA-1273 (Moderna) UTRs, CV2CoV (CureVac) UTRs, and a widely used human β-globin mRNA UTRs. We tested 14 different sequences of the coding region: sequences A–H for wet lab experiments, sequences from three main mRNA vaccine companies, MFE-opt. and CAI-opt. sequences (i.e., sequences with the lowest folding free energy and with CAI = 1, respectively), and the wildtype sequence. Most of the LinearDesign-generated mRNA sequences (sequences A–F and MFE-opt.) form fewer base pairs with UTRs. The folding free energies and structures are predicted by Vienna RNAfold (-d0 mode); MFEs of CDS are calculated without stop codon.