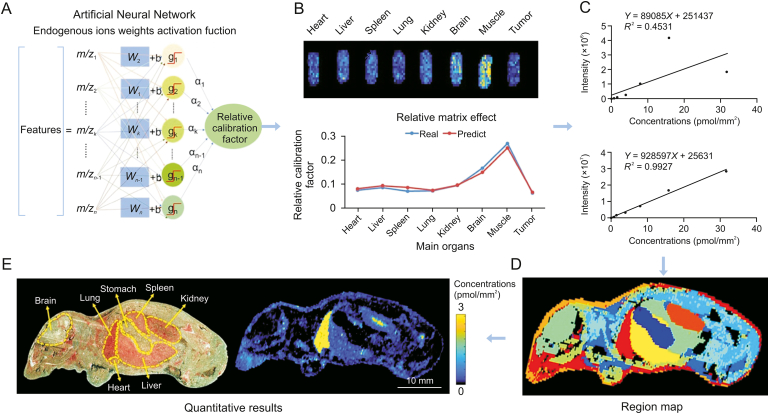
Fig. 5.
Application of the virtual calibration quantitative mass spectrometry imaging strategy to visualize antitumor drugs on whole-body animal sections. (A) The machine learning method to predict the relative calibration factor based on the endogenous metabolites. (B) The imaging of relative calibration factors of different organs (top) and the comparison between predicted and true values of the relative calibration factor (bottom). (C) The non-calibration and virtual calibration standard curves constructed with the drug amount versus the non-calibrated (top) and calibrated (bottom) drug ion intensities, respectively. (D) The image of whole-body sample segmentation by automatic pixel labelling using K-means and t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE) clustering analysis. (E) The result of drug quantitative visualization and the optical image of the sample. Reprinted from Ref. [128] with permission.