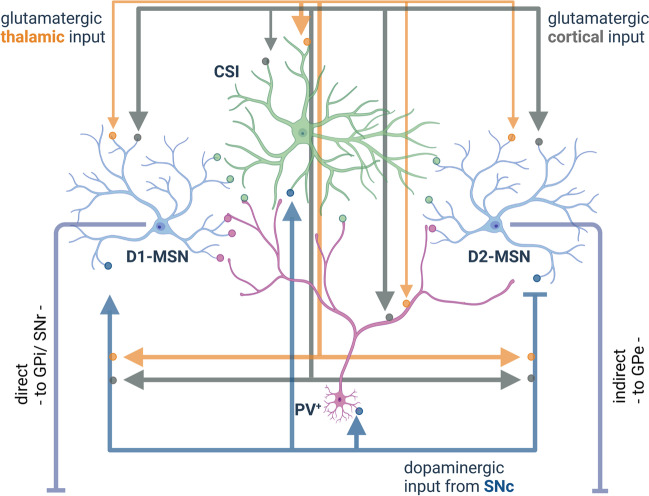
Fig. 2.
The intrastriatal network. The striatum plays an essential role within the movement loop and relays the glutamatergic cortical input. The striatal output to GPi (direct pathway) and the GPe (indirect pathway) is mediated through GABAergic projection neurons (medium spiny neurons, MSN), in which D1 or D2 receptors predominate, respectively. This striatal inhibitory output is modulated e.g. by GABAergic (PV+; parvalbumin-positive, purple) and cholinergic (CSI, green) interneurons as well as dopaminergic input (blue) from the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc), glutamatergic thalamic, and cortical inputs. The small dots on the neurons and connections represent the appropriate dopaminergic, glutamatergic, and GABAergic synapses (figure created with BioRender.com)