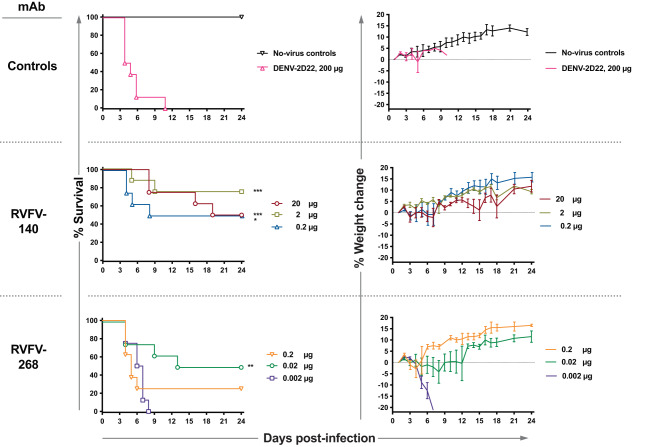
Fig. 5. Monotherapy is effective at low doses against RVFV infection in the BALB/c mouse model.
A single dose of mAb was administered by the IP route to mice (n = 8 per group) at 2 d.p.i. The virus was administered by SC inoculation of 300 PFU of RVFV strain ZH501. RVFV-268, RVFV-140, or DENV-2D22 (an isotype-matched negative control mAb) were tested in a sequential dose-down study design in this stringent therapeutic model of infection. Doses administered for RVFV-140: 20 µg, 2 µg, or 0.2 µg. Doses administered for RVFV-268: 0.2 µg, 0.02 µg, or 0.002 µg. Kaplan–Meier survival plots were statistically analyzed using a log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test where mAb-treated animals (***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05) were compared to animals treated with the DENV-2D22 negative control mAb. Weight graphs reflect group means standard error of the means of the percent change in weight of animals relative to body weight obtained the day after virus challenge. Sham-infected no virus controls are shown. Median survival for each condition tested: no-virus control—Undefined; DENV-2D22—4.5 days; 20 µg RVFV-140—21.5 days; 2 µg RVFV-140—Undefined days; 0.2 µg RVFV-140—16 days; 0.2 µg RVFV-268—5 days; 0.02 µg RVFV-268—18.5 days; 0.002 µg RVFV-268—6.5 days. P values for each condition tested compared to the DENV-2D22 control treated group using a Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test: no-virus control—0.0018; 20 µg RVFV-140—0.0002; 2 µg RVFV-140—0.0009; 0.2 µg RVFV-140—0.0345; 0.2 µg RVFV-268—0.3770; 0.02 µg RVFV-268—0.0084; 0.002 µg RVFV-268 –0.4403. Source data are provided as a Source data file.