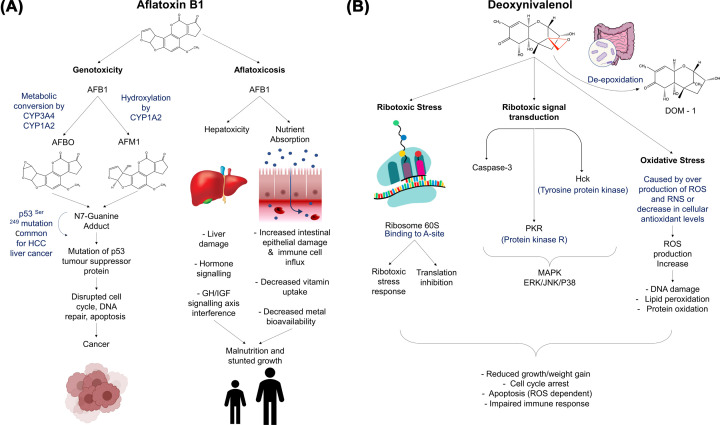
Figure 2. Mechanism of AFB1 induced cancer, malnutrition and stunted growth, and DON induced impairment of immune response, cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis.
(A) AFB1 causes genotoxicity through the conversion and hydroxylation of AFB1 to AFBO and AFM1, resulting in mutation in the tumour-suppression protein p53. AFB1 additionally causes hepatoxicity and interferes with nutrient absorption, resulting in cancer and growth reduction. (B) DON can be de-epoxidated into DOM-1 by gut bacteria that is less stable than DON and does not cause the ribotoxic stress response. DON can cause ribotoxic stress and interfere with translation inhibition. DON activates PKR and HcK resulting in increased MAPK. Oxidative stress is caused by increased ROS and RNS, and results in DNA damage, and protein oxidation whereby this leads to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis and impairment of immune response.