Fig 1.
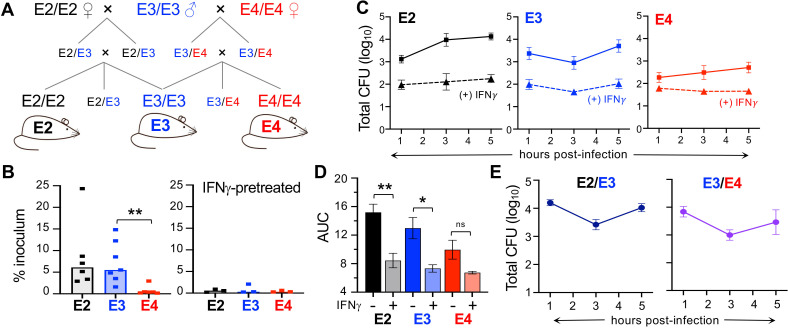
Bone-marrow-derived macrophages from aged homozygous APOE4/APOE4 (E4) mice are more resistant to L. monocytogenes infection than cells from APOE3/APOE3 (E3) or APOE2/APOE2 (E2) mice. (A) Breeding scheme for the rederivation of humanized homozygous APOE mice. (B) Invasion assay for macrophages pretreated with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; left) or IFNγ (right) for 24 h then infected with L. monocytogenes at MOI = 0.1 for 1 h. Each symbol represents the mean value of triplicate samples obtained from cells derived from a single aged mouse; median values (bars) for pooled data from multiple experiments were analyzed by Mann-Whitney U test: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (C) Intracellular growth assay measuring gentamicin-resistant L. monocytogenes in macrophages ± IFNγ pretreatment. Symbols indicate colony forming unit values for cells derived from n = 6 different aged mice per genotype that were tested in triplicate (± SEM) in each assay; a representative growth curve for cells from one mouse per genotype. (D) Area under the curve (AUC) for the data points shown in panel C. Analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s multiple comparisons. (E) Intracellular growth assay for macrophages derived from APOE heterozygous mice. Mean values ± SEM for triplicate samples from one of three independent experiments are shown. For panels (B) and (C), all but one animal in each group was female; for panel (E), there were n = 6 female and n = 3 male E2/E3 mice, and all the E3/E4 mice were male.