Extended Data Fig. 7 |. Effects of single amino acid substitutions at positions 72, 94, 416 and 417 on ReO4− transport.
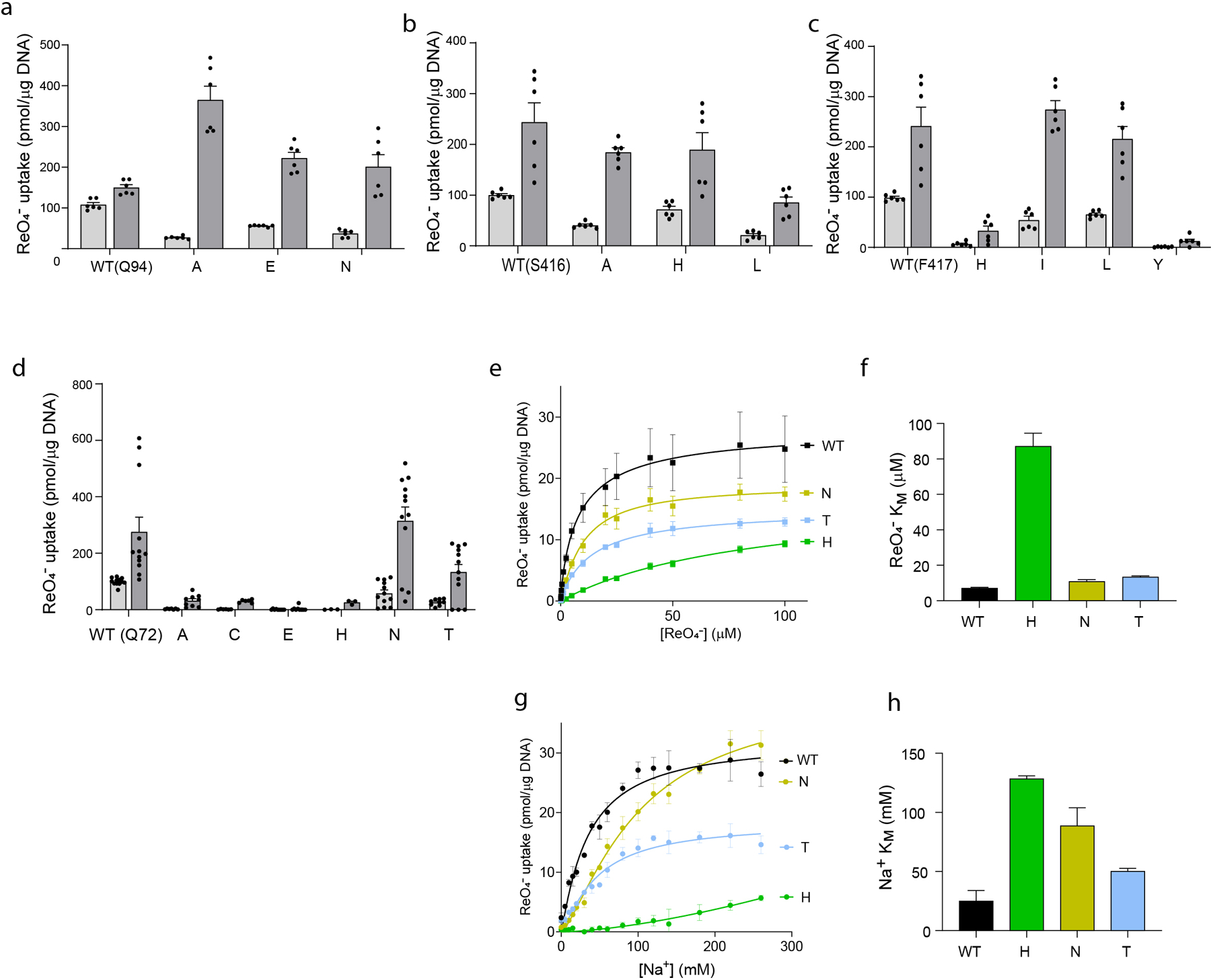
a-d. NIS-mediated ReO4− uptake at steady state. cDNA constructs coding for NIS mutants in which Q72 is replaced with the residues indicated were transfected into COS7 or HEK cells. ReO4− uptake by these NIS mutants was measured at 3 μM (light gray bars) and 30 μM (dark gray bars) ReO4− at 140 mM Na+ for 30 min with or without the NIS-specific inhibitor ClO4− (values obtained in the presence of ClO4− already subtracted). Results are given as pmols of ReO4− accumulated/μg DNA ± s.e.m. Values represent averages of the results from two or three different experiments, each of which was carried out in triplicate (n ≥ 6). e. Kinetic analysis of initial rates of ReO4− uptake (2-min time points) for Q72 NIS mutants determined at varying concentrations of extracellular ReO4− and varying concentrations of extracellular Na+. Results are given as pmols of ReO4− accumulated/μg DNA ± s.e.m. Values represent averages of the results from two or three different experiments, each of which was carried out in triplicate (n ≥ 6). f. ReO4− KM values determined from (e); error bars represent the standard deviation of the Michaelis-Menten analysis. g. Kinetic analysis of initial rates of ReO4− uptake (2-min time points) for Q72 NIS mutants determined at 100 μM ReO4− and varying concentrations of extracellular Na+. Results are given as pmols of ReO4− accumulated/μg DNA ± s.e.m. Values represent averages of the results from two or three different experiments, each of which was carried out in triplicate (n ≥ 6). h. Na+ KM values determined from (g); error bars represent the standard deviation of the Hill equation analysis.
