Figure 2.
The structural basis for Pol α-primase recruitment to the budding yeast replisome
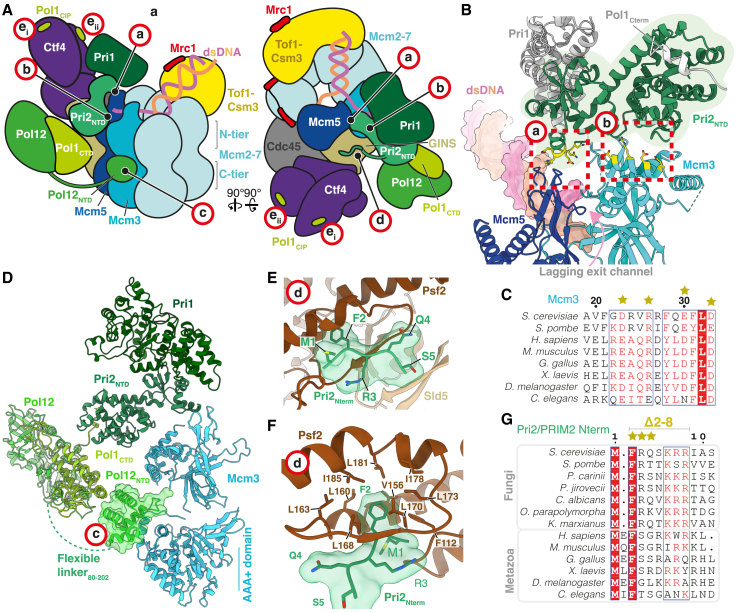
(A) Schematic of the budding yeast replisome highlighting Pol α-primase-binding sites (red circles labeled a–e).
(B) Atomic model highlighting the interfaces between Pri2NTD (green) and the Mcm5 (blue) zinc finger (site a) and Mcm3 (cyan) N-terminal helical domain (site b). Residues colored yellow with side chains displayed represent those targeted for mutational analysis.
(C) Multiple sequence alignment indicating the conservation of Mcm3 residues contacting Pri2NTD (site b), colored according to conservation. Stars correspond to the Mcm3 residues colored yellow in (B) that were mutated.
(D) Atomic model highlighting the interface between the Pol12NTD (green) and the Mcm3 (cyan) AAA+ domain in the MCM C-tier (site c).
(E) Atomic model highlighting the interface between the Pri2Nterm (green) and the Psf2 subunit of GINS (brown) (site d).
(F) Atomic model showing how Pri2-F2 projects into a hydrophobic pocket on Psf2, colored as in (E).
(G) Multiple sequence alignment of Pri2Nterm residues contacting Psf2. The alignment is grouped into fungal and metazoan sequences and colored according to conservation. Stars indicate residues mutated to alanine in the Pri2-AAA mutant.