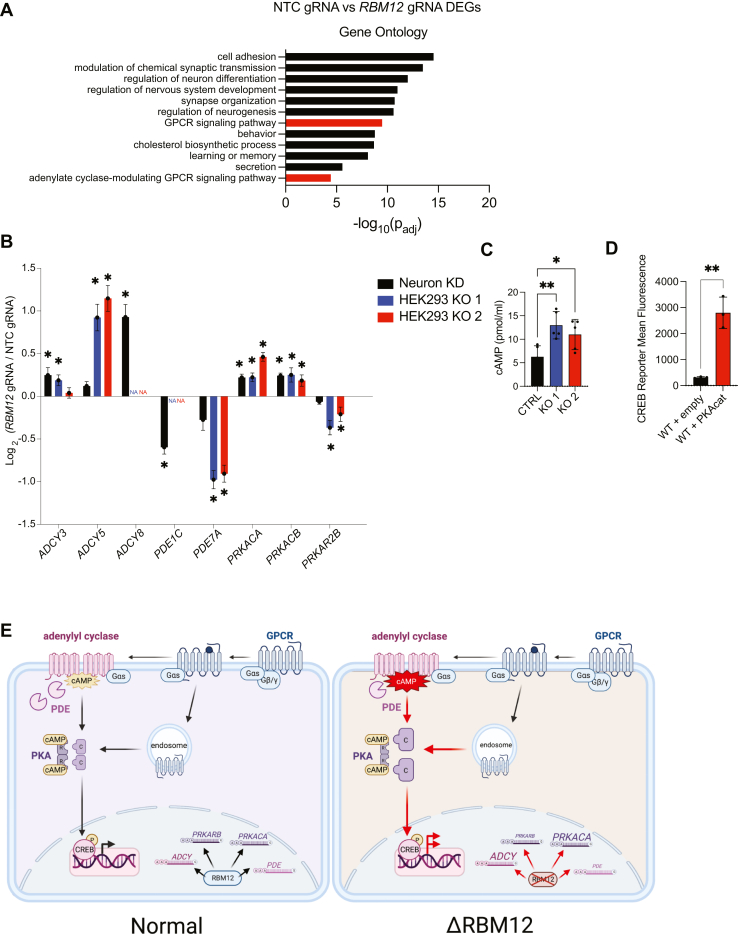
Figure 7.
RBM12 regulates the expression of multiple GPCR/cAMP effectors. A, gene ontology analysis of differentially expressed genes between WT and RBM12 KD neurons (n = 2645 genes). B, graph summarizing abundance changes (log2 fold change RBM12 gRNA/NTC gRNA) of known GPCR/cAMP regulators in WT and RBM12 KD neurons (n = 3 per cell line) and HEK293 (n = 7 in WT cells and n = 3 per KO cell line). Asterisks denote statistical significance (padj < 5.0 × 10–2 by Wald test). “NA” denotes genes not expressed in HEK293. C, basal cAMP levels in WT and HEK293 RBM12 KOs measured using ELISA assay (n = 5). All values are normalized relative to WT. D, flow cytometry measurement of the fluorescent CREB transcriptional reporter (CRE-DD-zsGreen) in WT cells expressing either empty plasmid or plasmid encoding PKAcat following stimulation with 1 μM Iso and 1 μM Shield for 4 h (n = 3). E, model of RBM12-dependent regulation of the GPCR/cAMP signaling pathway. All data are mean ± SD. Statistical significance was determined using Fisher’s exact test (A), adjusted p-value corrected for multiple testing by Wald test (B), one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s correction (C), or unpaired two-sided Student t test (D). ∗∗ = p < 0.01, ∗ = p < 0.05. GPCR, G protein–coupled receptor; RBM, RNA-binding motif; NTC, nontargeting control; PKAcat, PKA catalytic.