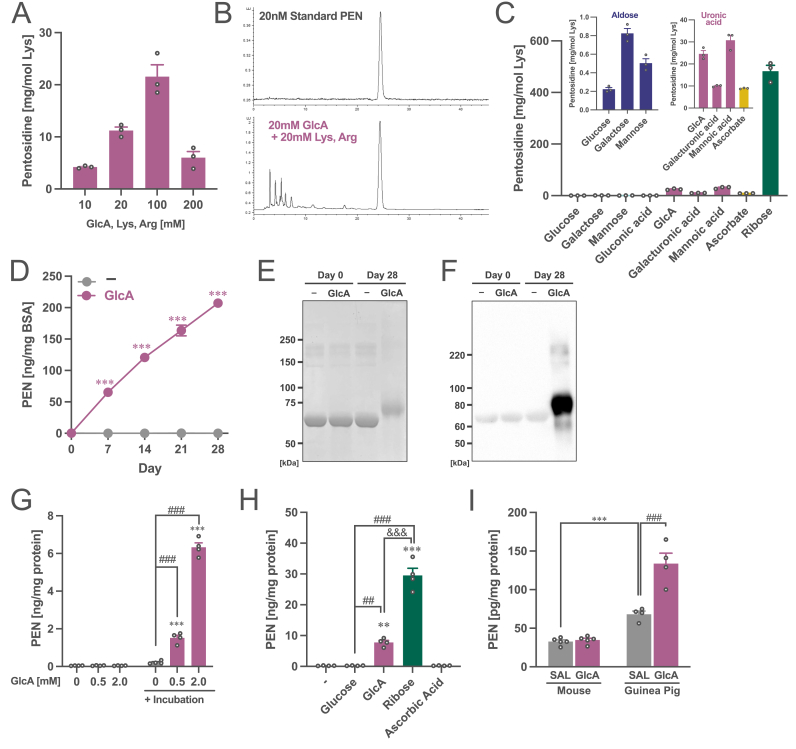
Fig. 2.
Generation of pentosidine from glucuronic acid. (A) Amount of the yielded PEN from GlcA by incubating with lysine and arginine. (B) Chromatograms of standard PEN and the incubate samples with GlcA, lysine, and arginine (20 mM each) for one week. (C) Amount of the yielded PEN from GlcA and aldoses, other uronic acids, and precursor molecules of PEN by incubating with lysine and arginine. Two enlarged figures of the data are included at the top. (D) Amount of the yielded PEN from GlcA by incubating with BSA. Two-way ANOVA: FInteraction(4,16) = 437, p < 0.001; FDay(4,16) = 436, p < 0.001; FGlcA(1,4) = 1296, p < 0.001. ***p < 0.001 (vs. control (−)) by Student’s t-test. (E) Staining with Coomassie brilliant blue and (F) western blotting with an anti-PEN antibody for BSA-PEN protein. (G) Amount of the yielded PEN from GlcA by incubating with human plasma. All the samples include plasma. Two-way ANOVA: FInteraction(2,6) = 858, p < 0.001; FGlcA(2,6) = 837, p < 0.001; FIncubation(1,3) = 446, p < 0.001. ***p < 0.001 (vs. without incubation), ###p < 0.001 (vs. 0 mM after incubation) by Tukey’s test. (H) Amount of the yielded PEN from GlcA and other precursor molecules of PEN by incubating with human plasma. One-way ANOVA: F(4,12) = 154, p < 0.001. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01 (vs. control (−)), ###p < 0.001, ##p < 0.01 (vs. Glucose) and &&&p < 0.001 (GlcA vs. Ribose) using Tukey’s multiple comparison test. (I) Quantification of PEN in plasma of saline (SAL)- or GlcA-treated mice and guinea pigs. Two-way ANOVA: FInteraction(1,14) = 24.6, p < 0.001; FSpecies(1,14) = 110, p < 0.001; FGlcA(1,14) = 27.8, p < 0.001. ***p < 0.001 (Mouse vs. Guinea pig with SAL), ###p < 0.001 (SAL vs. GlcA in Guinea pig) by Tukey’s test. The data are shown as mean ± SEM values. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)