Figure 2.
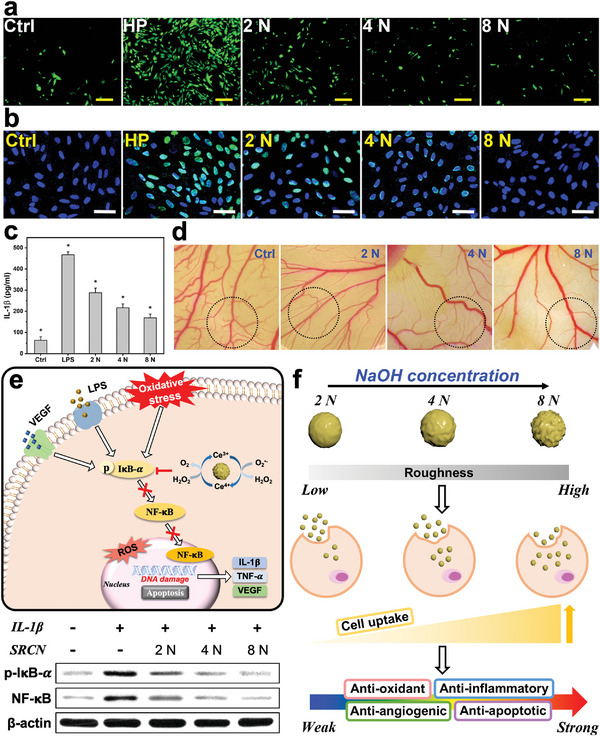
Bioactivity assays and mechanism of action studies. Effects of various types of SRCNs (2, 4, and 8 N) on suppression of H2O2 induced a) ROS production and b) cell apoptosis. RCKs were incubated with test SRCNs for 24 h and further exposure to H2O2 for 24 h; the cells incubated with no materials served as Ctrl. Levels of c) IL‐1β released from RCK cultures after incubation with various SRCN samples for 24 h. Values are mean ± SD (n = 5); *P < 0.05 versus all groups. d) Typical light micrographs of CAM vasculature after exposure to cellulose filter paper discs with tested SRCNs for 24 h. Dotted circles represent the areas of the CAM under the cellulose filter paper discs; Ctrl: cellulose filter paper discs without the SRCN pretreatment. e) Schematic illustration of the biological effects and mechanism of action via suppressing NF‐κB pathway of the SRCNs. Western blot analysis of p‐IκB‐α and NF‐κB expression in RCK cultures after a 24 h‐exposure to various SRCN samples. f) Demonstration of different types of SRCNs and their cellular uptake efficiencies and biological effects. Scale bars in a,b) are 50 and 100 µm, respectively.
