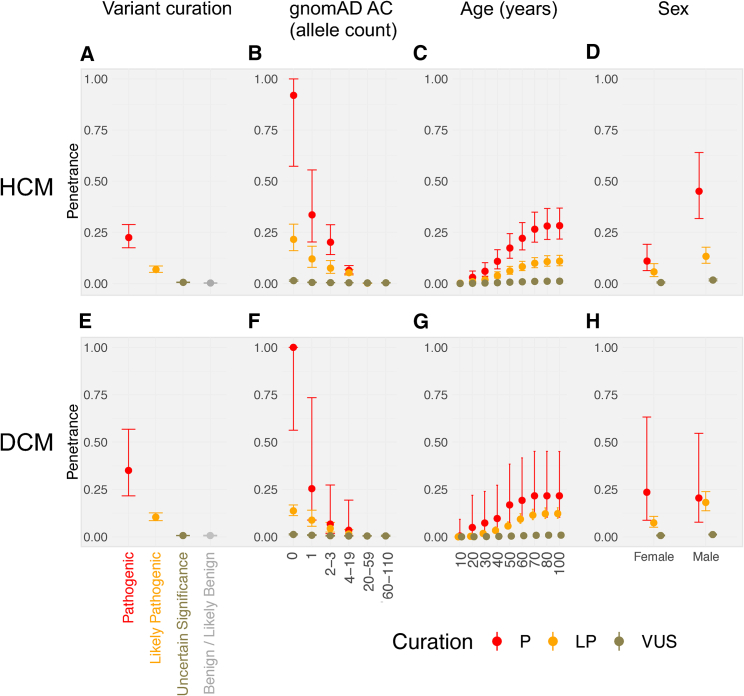
Figure 1.
Penetrance of rare variants in aggregate by variant curation, rarity, age, and sex
(A–H) In aggregate, variants curated as pathogenic and variants that are particularly rare (gnomAD allele count [AC] = 0) were most penetrant. The plot depicts aggregate estimated penetrance and 95% confidence intervals for rare variants in HCM- (A, B, C, D) and DCM-associated (E, F, G, H) genes. Variant curation was assessed following ACMG guidelines through ClinVar and CardioClassifier software with additional manual curation of variants with conflicting evidence (A and E [for HCM affected individuals: 173 P variants, 316 LP, 824 VUSs, 19 LB; for the UK Biobank: 30 P, 97 LP, 1,536 VUSs, 54 LB, 2 B; for DCM affected individuals: 21 P, 245 LP, 356 VUSs, 37 LB, 4 B; for the UK Biobank: 15 P, 505 LP, 3,933 VUSs, 108 LB, 7 B]). The variants were assessed for rarity by gnomAD AC bins, where 0 is not identified in the gnomAD dataset (B and F). Age was assessed in decades based on the cumulative proportion of affected individuals analyzed by each age timepoint (C and G). Sex was estimated with all parameters stratified by reported sex (D and H).