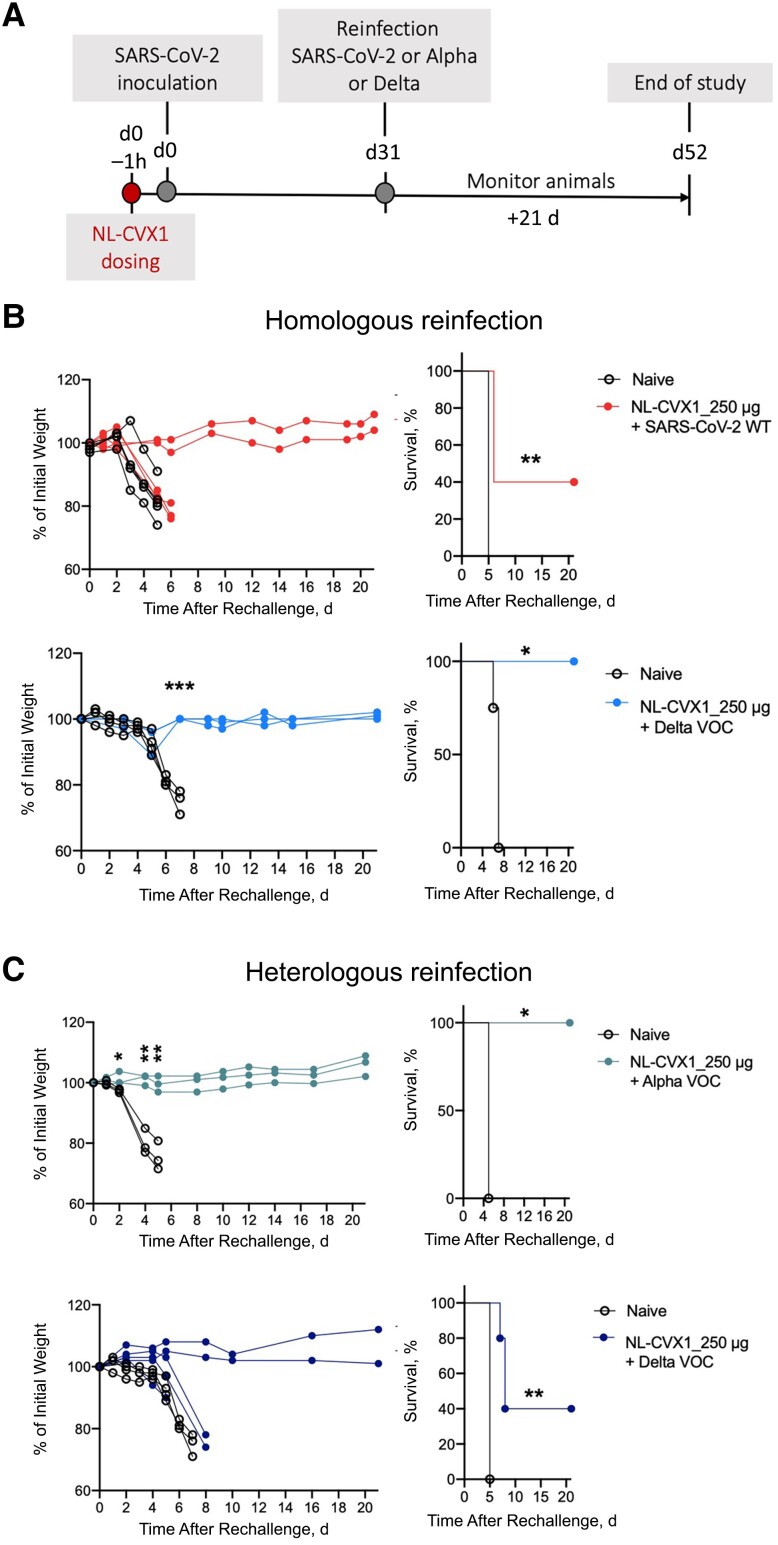
Figure 6.
Mice administered with a single prophylactic dose of NL-CVX1 show protection to reinfection. A, Female K18– human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (hACE2) mice, aged 7–11 weeks, were intranasally administered NL-CVX1 at 250 μg or vehicle, 1 hour (1h) before intranasal inoculation with 104 plaque-forming units (PFUs) of ancestral severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) or the Delta variant of concern (VOC). On day 31 (d31_ after infection, mice were reinfected with the same virus used for initial infection (homologous reinfection) or reinfected with a different variant (heterologous reinfection). Naive control mice (n = 3; clear circle) were never exposed to virus before and were infected for the first time with the same virus variant as the one used for reinfection. Mice were monitored for body weight loss, disease, and death for 21 days. B, Body weight change and percentage of survival in mice administered NL-CVX1 after homologous reinfection with ancestral SARS-CoV-2 virus (n = 5) or the Delta VOC (n = 5). C, Body weight change and percentage of survival of mice, initially infected with ancestral SARS-CoV-2 (wild type [WT]) and administered NL-CVX1, after heterologous reinfection with the Alpha (n = 3) or the Delta (n = 5) VOC. Body weight changes in experimental groups were statistically compared using multiple t tests, and survival rates were compared using Mantel-Cox tests. *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001.