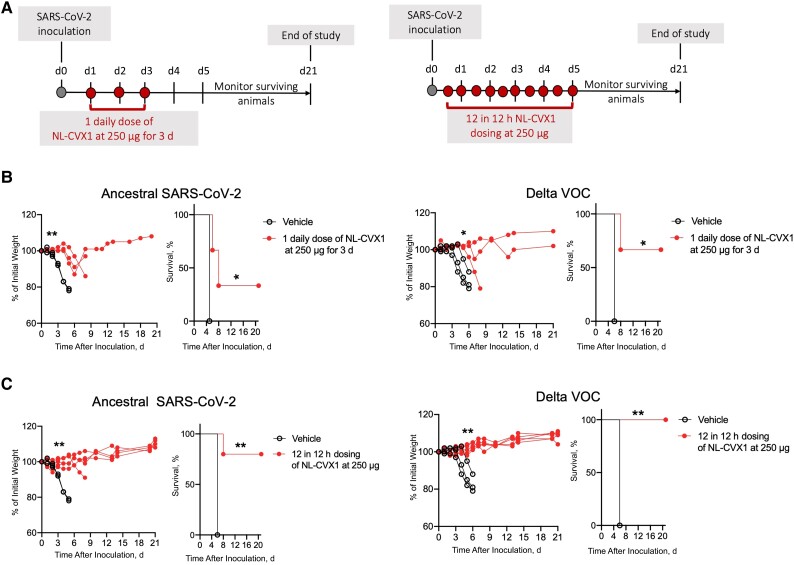
Figure 7.
Postexposure therapy with NL-CVX1 reduces severe disease in mice infected with ancestral severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus and the Delta variant of concern (VOC). A, Postexposure therapy study design. Female K18– human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 mice, aged 7–11 weeks, were intranasally administered NL-CVX1 at 250 μg or vehicle on days 1, 2, and 3 after infection or every 12 hours for 5 days. Mice were monitored for weight loss, disease, and death for 21 days. B, Body weight change and percentage of survival in mice infected with ancestral SARS-CoV-2 or the Delta VOC after administration of vehicle (clear circle; n = 3) or 3 doses of NL-CVX1 250 μg for 3 days (filled circle; n = 3). C, Body weight change and percentage of survival in mice infected with ancestral SARS-CoV-2 or the Delta VOC after administration of vehicle (clear circle; n = 3) or NL-CVX1 250 μg (filled circle; n = 5) every 12 hours after infection, for 5 days. Body weight changes were statistically compared using multiple t tests, and survival rates were compared using Mantel-Cox tests. *P < .05; **P < .01.