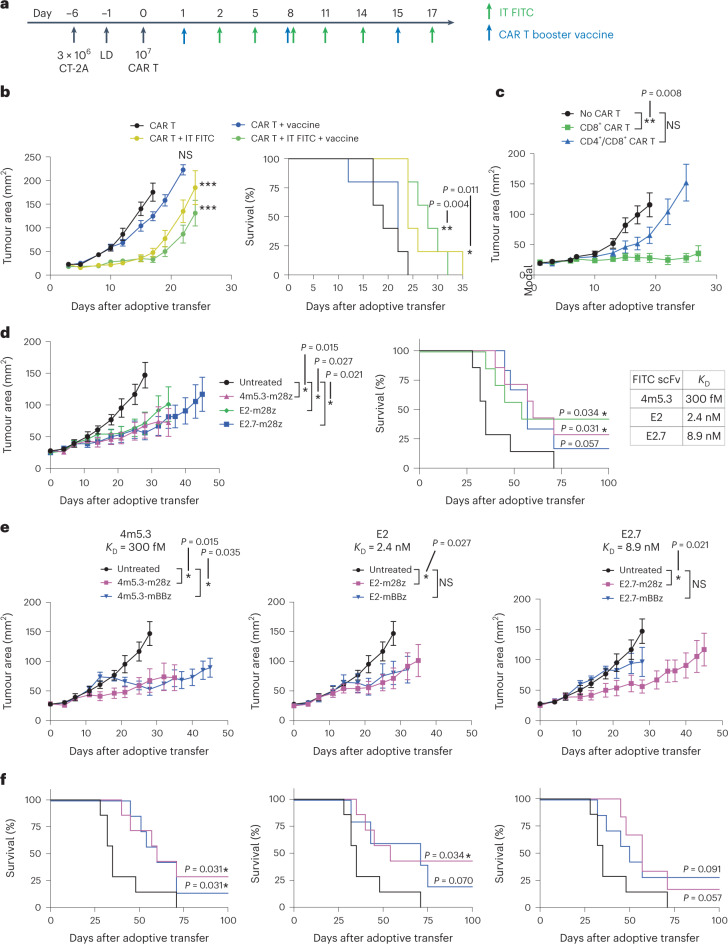
Fig. 4. Murine FITC CAR T cells combined with i.t. amph-FITC have therapeutic activity in models of melanoma and glioma.
a, Schematic and timeline of therapy for CT-2A tumour therapy. b, Tumour growth and overall survival of C57BL/6 mice (n = 5 animals per group) bearing B16F10 tumours treated with E2-28z CAR T cells as in Fig. 3a with indicated combinations. c, Tumour growth of CT-2A tumour-bearing C57BL/6 mice (n = 5 animals per group) treated with amph-FITC, FITC CAR T cells and vaccine composed of only CD8+ T cells or a combination of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. d, Tumour growth and survival following treatment of CT-2A tumour-bearing mice (n = 5 animals per group) with CARs with low (E2.7), medium (E2) and high (4m5.3) affinities for FITC, including i.t. amph-FITC and vaccine. e,f, Tumour growth (e) and survival (f) of CT-2A tumour-bearing mice treated with CARs bearing CD28 or 4-1BB co-stimulatory domains across a range of binding affinities in combination with IT amph-FITC and amph-FITC vaccination (n = 5 animals per group). Error bars represent standard error of the mean. All replicates are biological replicates. P values were determined by two-way ANOVA (tumour growth curves) and log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test (survival curves). NS, not significant; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.