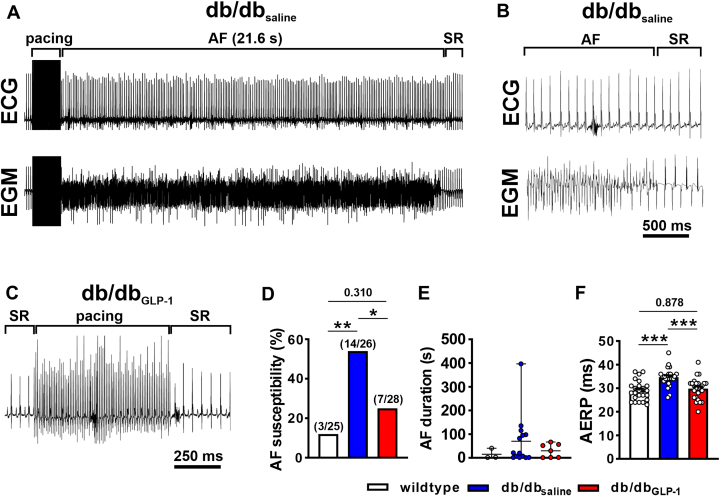
Figure 1.
Effects of chronic GLP-1 Treatment on AF and AERP in db/db Mice
(A) Representative surface electrocardiogram (ECG) (top) and atrial intracardiac electrogram (EGM) (lower) showing the induction of atrial fibrillation (AF) following burst pacing in an anesthetized db/db mouse after 4 weeks of saline infusion. AF lasted for 21.6 seconds and then reverted to sinus rhythm (SR). (B) Magnified view of the recording shown in A illustrating AF converting to SR. (C) Representative surface ECG showing the absence of AF induction after burst pacing in a db/db mouse infused with glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) for 4 weeks. (D) Inducibility of AF in wild-type mice, db/db mice infused with saline (db/dbsaline), and db/db mice infused with GLP-1 (db/dbGLP-1) for 4 weeks. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of mice induced into AF. Data analyzed by Fisher exact test. (E) Duration of AF in the wild-type, db/dbsaline, and db/dbGLP-1 mice that were induced into AF. (F) Atrial effective refractory period (AERP) in wild-type (n = 25), db/dbsaline (n = 26), and db/dbGLP-1 (n = 28) mice. Data analyzed by one-way analysis of variance with Holm-Sidak post hoc test. ∗P< 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001.