FIGURE 8.
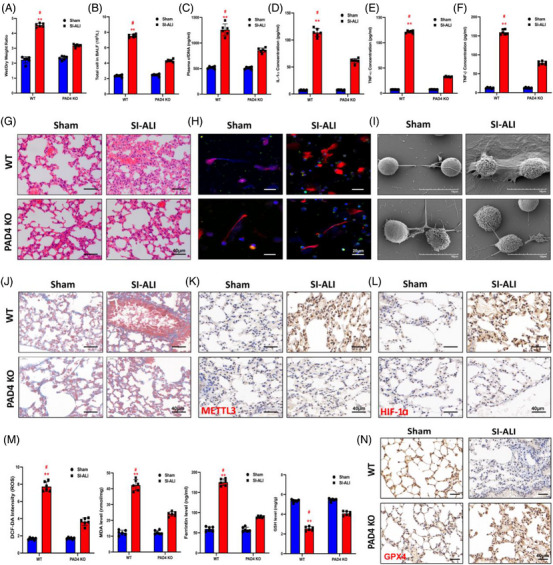
Peptidyl arginine deiminase 4 (PAD4) knockout alleviates ferroptosis in alveolar epithelial cells and sepsis‐induced acute lung injury (SI‐ALI). (A) The degree of lung damage was evaluated by wet/dry ratio from wild‐type (WT) and PAD4 knockout (KO) mice in sham and SI‐ALI groups (n = 6 in each group). (B) Cell counting (n = 6 in each group) measured total cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). (C) Plasma cfDNA evaluated neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation from WT and PAD4 KO mice in sham and SI‐ALI groups (n = 6 in each group). (D–F) Interleukin (IL)‐1α, tumour necrosis factor (TNF)‐α and TNF‐β evaluated the degree of systemic inflammation. (G) Images from haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of lung tissues evaluated the degree of lung damage. Images from immunofluorescence (IF) assay (H) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (I) evaluated the level of NETs. (J) The degree of lung fibrosis was evaluated by Masson staining analysis. The levels of METTL3 (K), hypoxia‐inducible factor‐1α (HIF‐1α) (L) and glutathione‐peroxidase 4 (GPX4) (N) were evaluated by IHC. (M) The level of ferroptosis was evaluated by reactive oxygen species (ROS), MDA, ferritin and glutathione (GSH) (n = 6 in each group). ** p < .01. #SI‐ALI versus Sham (two‐way analysis of variance [ANOVA] with Tukey's correction).
