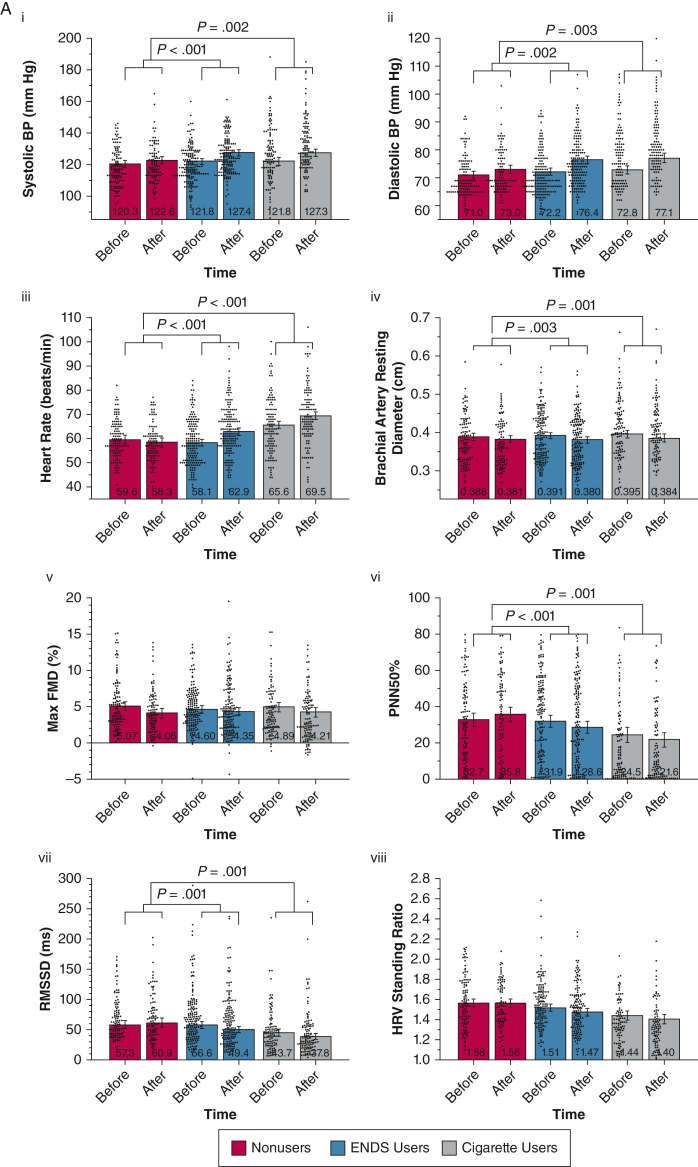
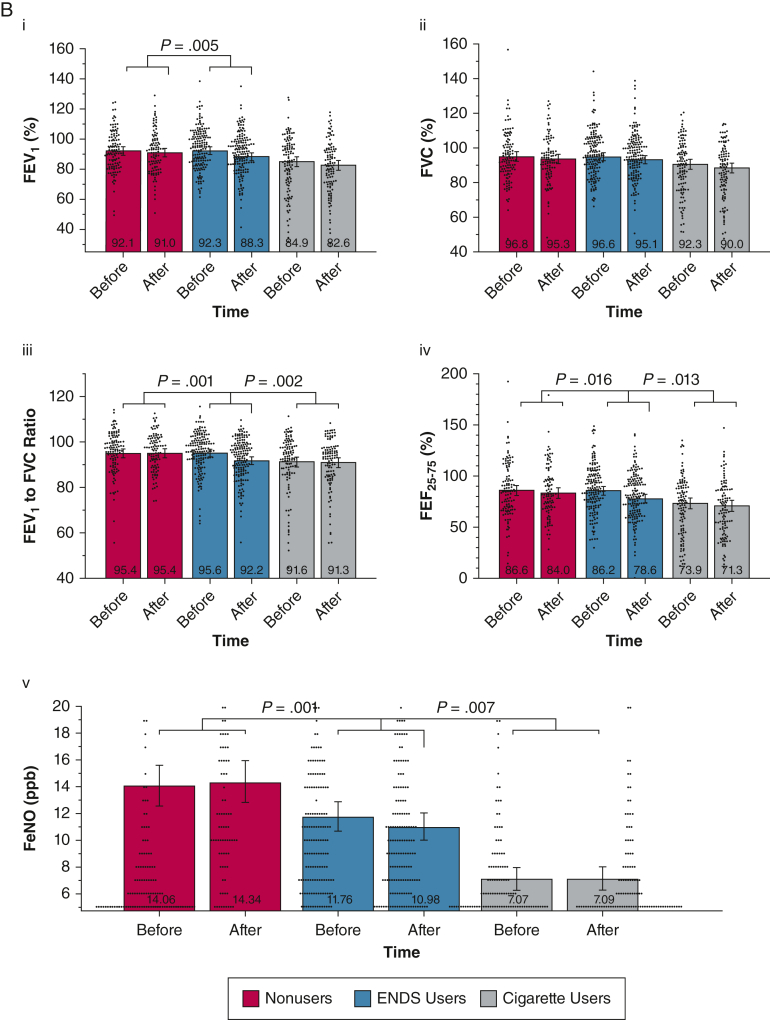
Figure 1.
A, B, Combined violin and bar plots showing cardiovascular and pulmonary measurements obtained before and after the nicotine-containing product challenge: cardiovascular measures (A) and pulmonary measures (B). Linear mixed models adjusted for age, sex, and race or ethnicity compared the within-group and between-group responses after product use. Violin plots show distributions of observed outcomes for within each group and time point. Bar plots depict model-estimated marginal means and associated 95% CIs with covariates fixed at their mean values. P value annotations reflect effects associated with specific group × time contrasts (e-Tables 1-20). False discovery rate correction using the Benjamini and Hochberg procedure was applied to all 17 cardiovascular and pulmonary product challenge tests. All nominally significant effects in this set survived false discovery rate correction and were followed by specific group contrasts. ENDS = electronic nicotine delivery system; Feno, fractional exhaled nitric oxide; FMD = flow-mediated dilation; HRV = heart rate variability; PNN50% = percentage of successive R-R intervals that differ by > 50 ms; RMSSD = root mean square differences in successive normal intervals.