Abstract
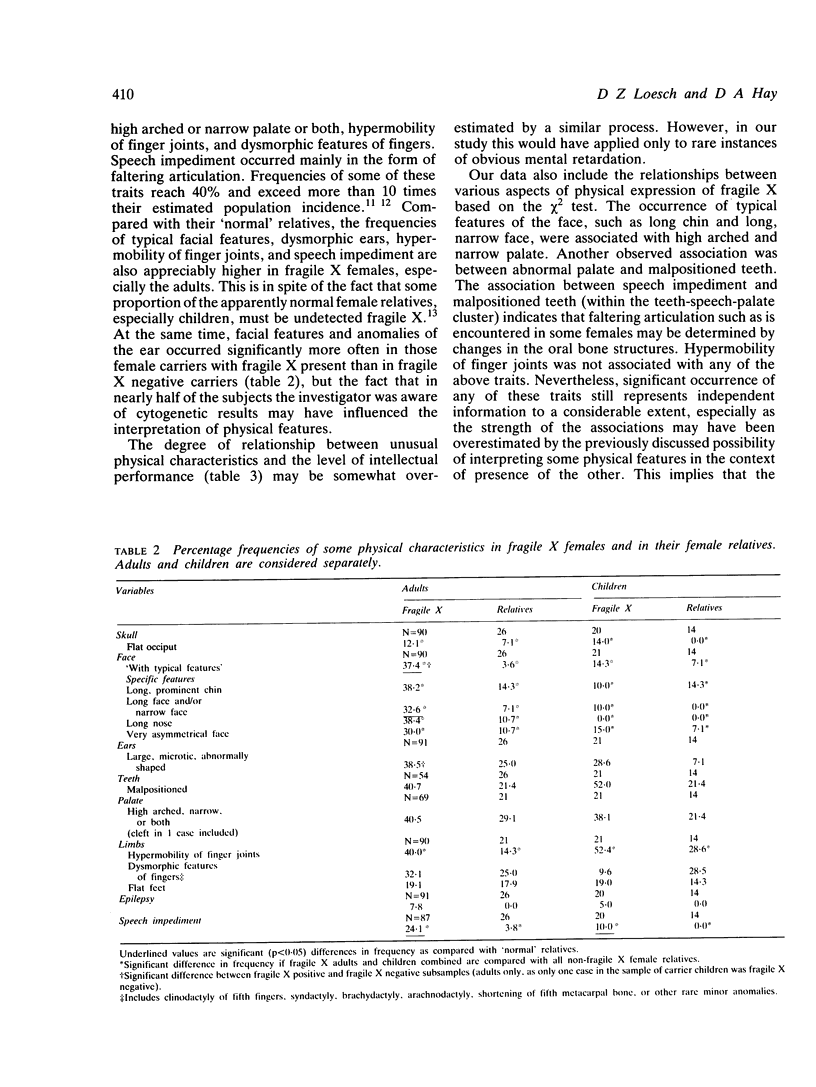
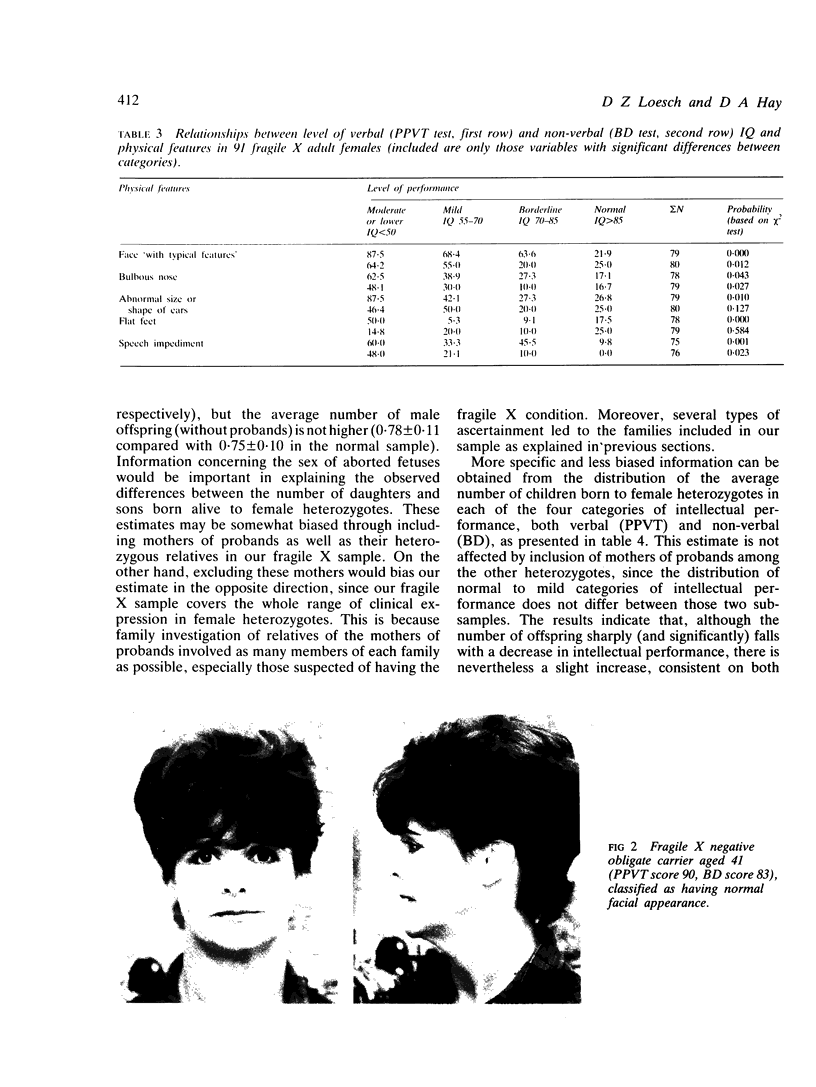
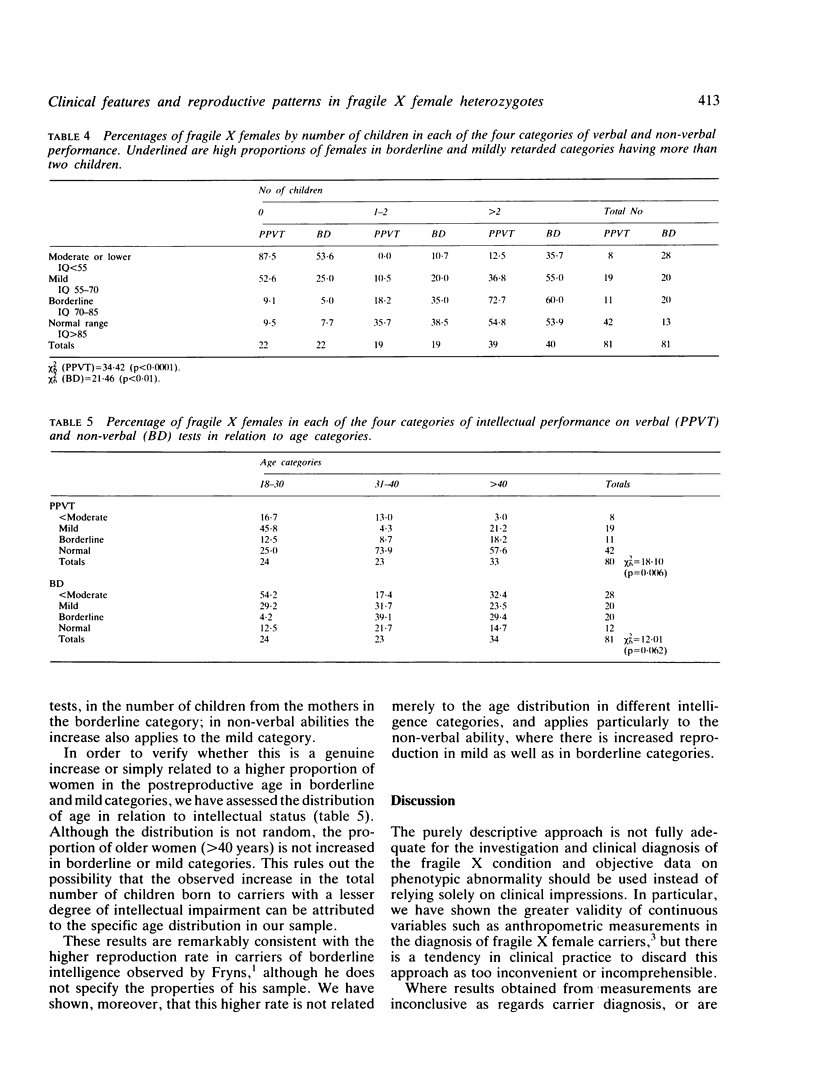
Clinical findings are presented on 113 fragile X female heterozygotes from 44 families, based on physical examination, behavioural assessment, and reproductive history. In 85% of a subsample of 92 adult females non-verbal IQ score derived from the Block Design test was 85 or less. Verbal ability deficits were much less common. Typical facial characteristics, irregular teeth, and hypermobility of finger joints occurred in approximately 40% of adult females, but facial abnormalities were less common in children. Some physical anomalies and the level of intellectual impairment were, in adult carriers, associated with the presence of fragile X sites. The commoner physical anomalies or typical facial characteristics and intellectual abilities differed significantly between the known female heterozygotes and their 40 presumed normal relatives. Frequency of miscarriages was increased in fragile X females; in spite of this, a moderate increase in the number of children has been encountered in female carriers with borderline intellectual impairment. This important problem has genetical implications and needs further investigation. The importance is emphasised of a more detailed clinical examination of the females at risk in fragile X families.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fryns J. P. The female and the fragile X. A study of 144 obligate female carriers. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Jan-Feb;23(1-2):157–169. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320230110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper M. B., Hagerman R. J., Ahmad R. S., Mariner R. Cognitive profiles and the spectrum of clinical manifestations in heterozygous fra (X) females. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Jan-Feb;23(1-2):139–156. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320230109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesch D. Z., Hay D. A., Sutherland G. R., Halliday J., Judge C., Webb G. C. Phenotypic variation in male-transmitted fragile X: genetic inferences. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Jun;27(2):401–417. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320270219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARDEN P. M., SMITH D. W., MCDONALD M. J. CONGENITAL ANOMALIES IN THE NEWBORN INFANT, INCLUDING MINOR VARIATIONS. A STUDY OF 4,412 BABIES BY SURFACE EXAMINATION FOR ANOMALIES AND BUCCAL SMEAR FOR SEX CHROMATIN. J Pediatr. 1964 Mar;64:357–371. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(64)80188-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. L., Jacobs P. A., Morton N. E., Froster-Iskenius U., Howard-Peebles P. N., Nielsen K. B., Partington M. W., Sutherland G. R., Turner G., Watson M. Further segregation analysis of the fragile X syndrome with special reference to transmitting males. Hum Genet. 1985;69(4):289–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00291644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. L., Morton N. E., Jacobs P. A., Turner G. The marker (X) syndrome: a cytogenetic and genetic analysis. Ann Hum Genet. 1984 Jan;48(Pt 1):21–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1984.tb00830.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theobald T. M., Hay D. A., Judge C. Individual variation and specific cognitive deficits in the fra(X) syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Sep;28(1):1–11. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Jacobs P. Marker (X)-linked mental retardation. Adv Hum Genet. 1983;13:83–112. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8342-4_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel F. Mutation and selection in the marker (X) syndrome. A hypothesis. Ann Hum Genet. 1984 Oct;48(Pt 4):327–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1984.tb00846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb G. C. Detection of the fragile X chromosome and other fragile sites. Clin Genet. 1985 May;27(5):520–521. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1985.tb00243.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




