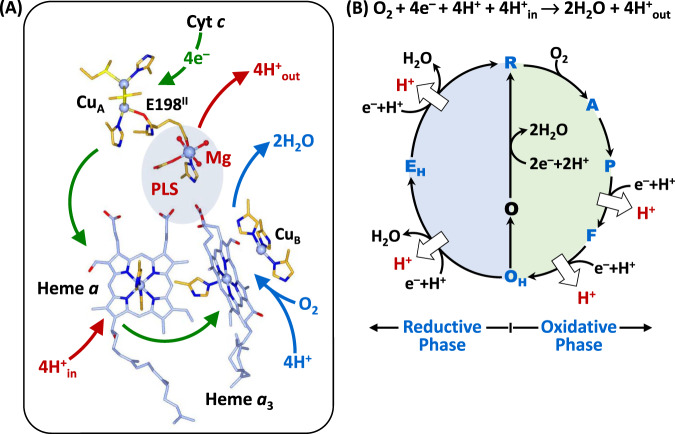
Fig. 1. Oxygen reduction reaction catalyzed by bCcO.
A Schematic illustration of the four redox active metal centers in bCcO and the electron and proton transfers associated with the O2 reduction reaction. The entry of O2 and four substrate protons into the heme a3/CuB binuclear center (BNC), as well as the release of the product water molecules out of it, are indicated by the blue arrows. The associated entry of four electrons into the BNC and the translocation of four pumped protons across the membrane are indicated by the green and red arrows, respectively. The putative proton loading site (PLS) between heme a3 and the Mg center is highlighted by the light blue background. B The overall O2 reduction reaction and the associated mechanism. The P intermediate is a general term for the PM and PR intermediates. The entry of the electrons and substrate protons into the BNC and the release of the product water molecules are indicated in each step of the reaction as described in the main text. The coupled proton translocation reactions are indicated by the white arrows. If the OH intermediate produced at the end of the oxidative phase is allowed to relax to the resting O state, its reduction to R does not support proton translocation.