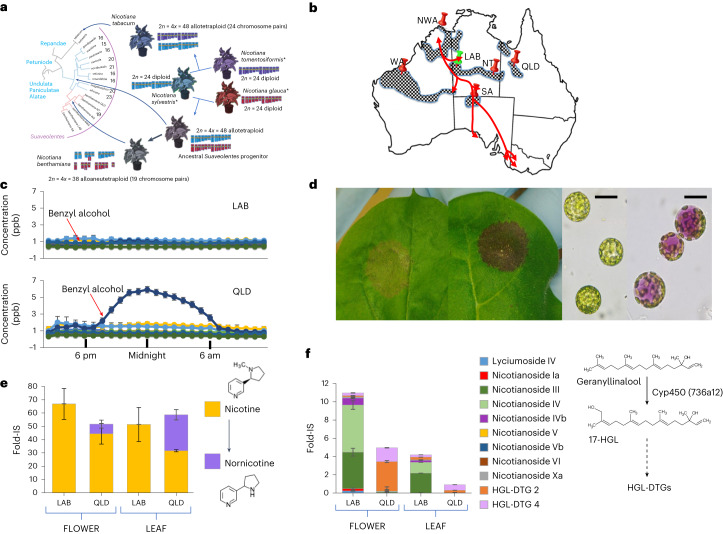
Fig. 1. Phenotypic and biochemical diversity of N. benthamiana.
a, Proposed phylogeny and origin of the Suaveolentes section compared with other Nicotianas. Chromosome numbers are indicated for each Suaveolentes species. Species highlighted by an asterisk are extant relatives of the putative parents of N. benthamiana and N. tabacum. b, Distribution of N. benthamiana in Australia (chequered regions). The physical locations of isolated N. benthamiana accessions reported in this study are shown by pins, and traditional indigenous trading routes are shown by red lines. c, Profiles of average emission of selected floral volatile compounds from LAB and QLD over a 24-h period. Dark blue, benzyl alcohol. For other compounds see Extended Data Fig. 1. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. (n = 4 per sample point). d, Anthocyanin production 5 days after transient expression of AN-like MYB in LAB and QLD; right-hand panels show protoplasts isolated from LAB and QLD infiltrated patches (n = 5). Scale bar, 50 μm. e, Comparison of the accumulation of nicotine and nornicotine in flowers and leaves of LAB and QLD. The biochemical conversion of nicotine to nornicotine, mediated by the CYP82E demethylase (Extended Data Fig. 9), is shown on the right. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. (n = 4). f, Comparison of the accumulation of HGL-DTGs in flowers and leaves of LAB and QLD. The schematic biochemical pathway is shown on the right. Data are presented as mean ± s.d. (n = 4).