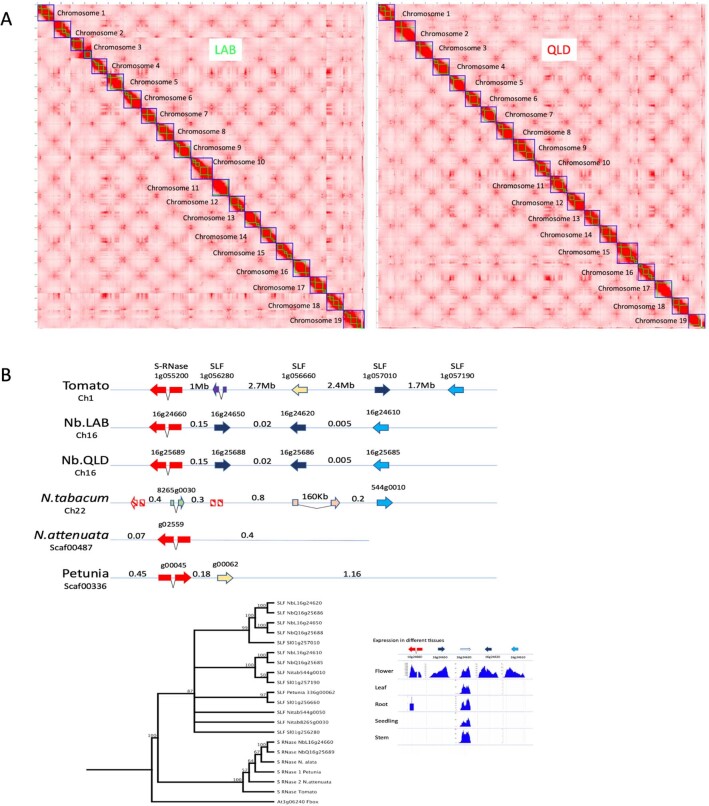
Extended Data Fig. 4. (A).Plot of contact matrices of LAB and QLD assemblies. (B).Synteny of Self-incompatibility (S)-like loci in tomato, N. attenuata, N.tabacum, petunia, LAB and QLD, cladogram of gene sequence similarities and tissue- expression of mRNA LAB S-locus genes.
(a) Plot of contact matrices of LAB and QLD assemblies. Juicebox plot from HiC analysis showing resolution into 19 contiguous elements (chromosomes) for both LAB and QLD assemblies. (b) Synteny of self-incompatibility (S)-like loci in tomato, N. attenuata, N.tabacum, petunia, LAB and QLD, cladogram of protein gene sequence similarities and tissue-specific mRNA expression of the LAB S-locus. Gene arrangement and relationships in cartoon form of the genes in the highly recombinogenic S-locus (comprised of an S-RNAse and associated multiple copies of F-box (SLF) proteins) in the most advanced genome assemblies of tomato, N. attenuata, N.tabacum, petunia, LAB and QLD. The colours of the genes represent their relationships across species, as indicated in the cladogram. The analysis shows contiguity of the S-locus in tomato, LAB and QLD and the fragmented nature of the locus in N. attenuata, Petunia axillaris, due to their presence on small scaffolds, and the incomplete assembly of Ch22 in N.tabacum. Tissue expression data for LAB shows that the intervening gene 16g24630 is expressed in all 5 tissues examined but the S-RNAse and SLF genes are expressed only in the floral tissue, as expected for a floral incompatability-associated locus. Distances between genes are indicated in Mb.