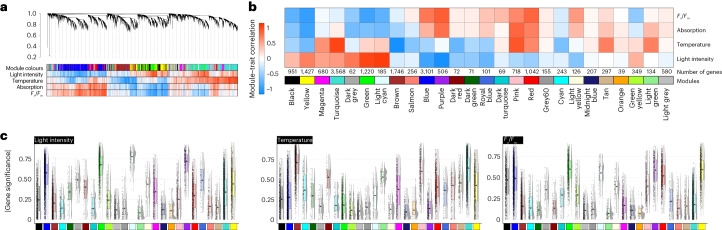
Fig. 4. Unsupervised gene expression clusters recover genetic programmes separated by environmental cues.
Gene expression clustering into 26 coloured modules was performed using WGCNA; grey is the module of unclustered genes. a, Hierarchical cluster tree of 17,095 genes. The heat map below the dendrogram and module colour assignment shows the gene significance measure (from red, positive correlation, to white, no correlation, to blue, negative correlation) for the four different conditions or physiological parameters. b, Heat map of the module–trait correlation based on eigengenes (from red, positive correlation, to white, no correlation, to blue, negative correlation); see Supplementary Fig. 7. c, Box plots of the mean gene significance across modules (given in the corresponding module colour) towards the parameters light intensity, temperature and Fv/Fm. The box plots display the interquartile range (IQR) of the data, compactly displaying the distribution of a continuous variable. They visualize five summary statistics (the median, two hinges and two whiskers). The upper whiskers extends from the hinges to the largest/smallest value no further than 1.5× IQR from the hinge. Each data point (n) is a gene, and the total n of genes is the same as shown in b. We calculated the gene significance for each gene using the WGCNA package and Pearson method.