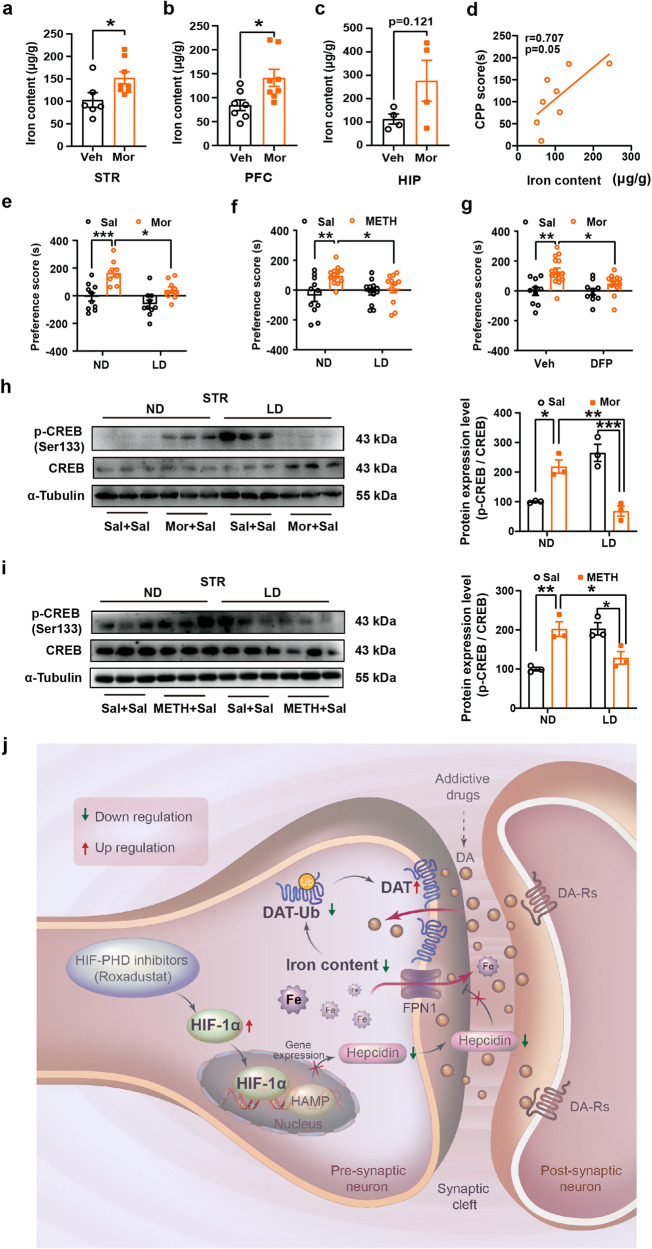
Fig. 7.
Iron deficiency inhibits Mor- and METH-induced CPP formation and phosphorylation of CREB. a-c Mouse brain tissues were collected within 24 h after Mor-CPP tests and prepares for ICP-MS detection of total iron content. Iron content was increased after Mor-CPP formation (a, Veh, n = 6, Mor, n = 8, t = 2.346, df = 12, P = 0.0370. b Sal, n = 7, Mor, n = 8, t = 2.628, df = 13, P = 0.0209. c Sal, n = 4, Mor, n = 4, t = 1.806, df = 6, P = 0.1209). d The correlation of iron content and CPP score was analyzed by correlation analysis. Iron content was correlated positively with Mor-CPP scores (n = 8, r = 0.707, P = 0.05). e, f WT mice were fed with low iron diet for 4 weeks as described in Methods. Low iron diet suppressed Mor- and METH-CPP acquisition as indicated by reduction in CPP scores (e, ND-Sal, n = 10, ND-Mor, n = 8, LD-Sal, n = 10, LD-Mor, n = 9; group, F(1,33) = 23.61, P < 0.0001; diet, F(1,33) = 9.514, P = 0.0041; group × diet, F(1,33) = 1.616, P = 0.2125. f ND-Sal, n = 11, ND-METH, n = 13, LD-Sal, n = 13, LD-METH, n = 12; group, F(1,45) = 9.155, P = 0.0041; diet, F(1,45) = 1.302, P = 0.2598; group × diet, F(1,45) = 4.769, P = 0.0342). g The bilateral cannula was implanted into PFC of mice brain 7 days prior to CPP performance, deferiprone (DFP) (13 mg/mL, 2 μL per site) was injected 6 h before morphine injection every day in conditioning phase. DFP pretreatment suppressed Mor-CPP acquisition as indicated by reduction in CPP scores (Veh-Sal, n = 10, Veh-Mor, n = 16, DFP-Sal, n = 10, DFP-Mor, n = 14; group, F(1,46) = 18.14, P = 0.0001; drug, F(1,46) = 3.751, P = 0.0589; group × diet, F(1,46) = 3.167, P = 0.0817). h, i Mice whole striatum tissues were collected 24 h after Mor- and METH-CPP tests for immunoblot assays, respectively. Low iron diet suppressed Mor- and METH-induced expression of (Ser133) phosphorylated-CREB in STR (h, n = 3, group, F(1,8) = 3.749, P = 0.0889; drug, F(1,8) = 0.1284, P = 0.7293; group × drug, F(1,8) = 61.05, P < 0.0001. i n = 3, group, F(1,8) = 0.8998, P = 0.3706; drug, F(1,8) = 0.9758, P = 0.3522; group × drug, F(1,8) = 35.83, P = 0.0003). j Schematic diagram of possible mechanisms underlying Rox-induced amelioration of drug dependence. Rox induces HIF-1α accumulation and nuclear translocation, thereby inhibiting hepcidin transcription. Iron efflux is enhanced by reduction of hepcidin mediated-FPN1 degradation. Finally, iron deficiency suppresses DAT ubiquitin degradation, thus decreasing DA concentration in the synaptic cleft and ultimately ameliorating drug dependence. The Schematic diagram was drawn by Adobe Illustrator software (Version 2022). Representative images for immunoblots are shown in the left panels and quantitative data are shown in the right panels. Values are presented as means ± SEM. Statistical analyses for a-c, and for d, and for e-i were performed using Student’s t-test and correlation analysis and two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni-corrected tests, respectively. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001