Figure 7. Model of AP site protection by coordinated formation and release of HMCES‐DPCs.
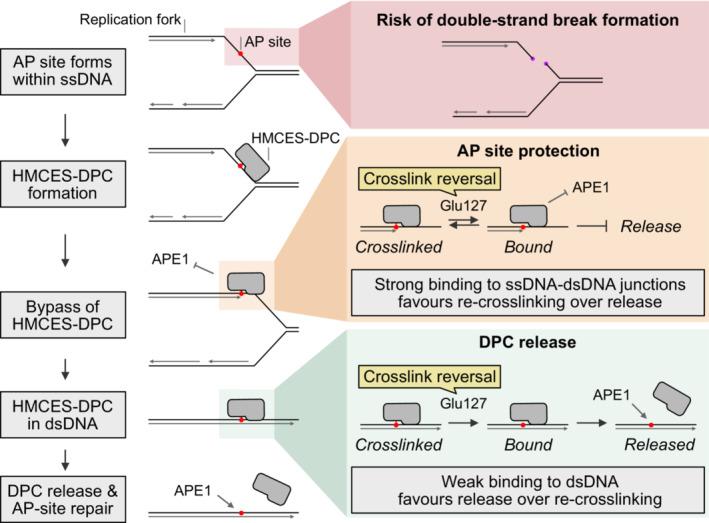
AP sites within ssDNA at the replication fork are dangerous because they can lead to the formation of toxic DNA double‐strand breaks. The conserved protein HMCES covalently crosslinks to AP sites in ssDNA to prevent strand scission.
HMCES‐DPCs efficiently protect AP sites in ssDNA and at ssDNA‐dsDNA junctions against spontaneous or enzymatic incisions. While the active site constantly cycles between a crosslinked and a non‐crosslinked state (catalysed by Glu127), HMCES affinity to the underlying DNA is high which favours re‐crosslinking over dissociation. In dsDNA, affinity is low which favours release of HMCES over re‐crosslinking and thereby enables APE1 endonuclease to initiate AP site repair in dsDNA.
