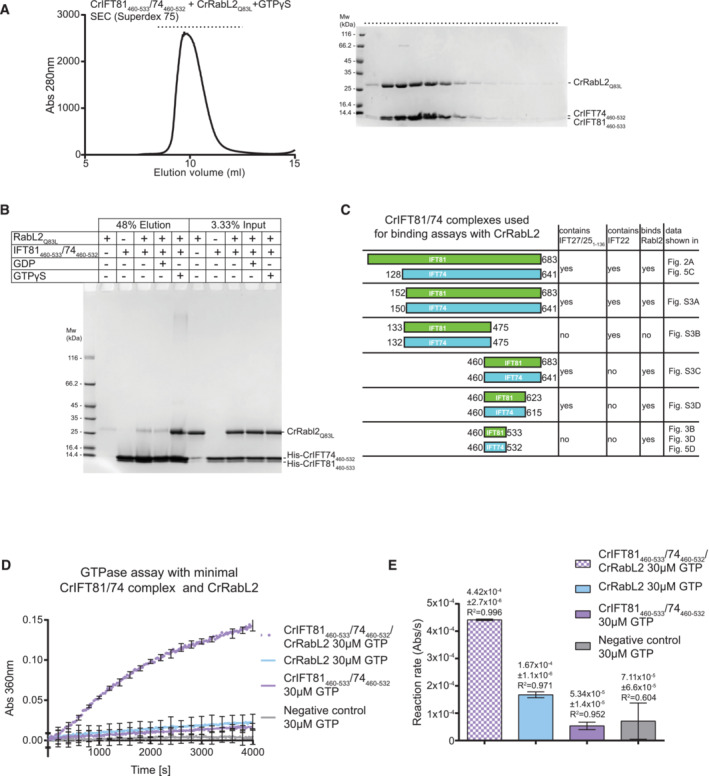
Figure 3. Mapping of a minimal CrIFT81460‐533/CrIFT74460‐532 complex that binds RabL2 and activates GTP hydrolysis.
-
ASEC profile showing that a minimal CrIFT81460‐533/CrIFT74460‐532 complex co‐purifies with CrRabL2Q83L in the presence of GTPγS (left). The right panel displays the Coomassie‐stained SDS gel of SEC fractions (horizontal top dashed line).
-
BAn N‐terminal hexa‐histidine‐tagged CrIFT81460‐533/74460‐532 complex interacts with untagged CrRabL2Q83L in a GTPγS‐dependent manner in pull‐down assays.
-
CSchematic of all CrIFT81/74 truncations used in this study for CrRabL2‐binding assays. The presence of CrIFT27/251‐136 and/or CrIFT22 in a complex with the CrIFT81/74 variants as well as their ability to bind CrRabl2 are indicated.
-
DGTPase assay using CrRabL2 and a minimal IFT81/74 complex show stimulation of GTP hydrolysis. Concentrations for each experiment were 60 μM protein and 30 μM GTP. Each experiment was done in three technical replicates; curves represent the averages with error bars representing standard deviations each 200 s.
-
EQuantification of GTPase reaction rates (arbitrary units of absorbance [Abs] per second [s]) using single exponential fit (D); error bars and R 2‐value indicate the agreement of the fit to the curves in (D).
