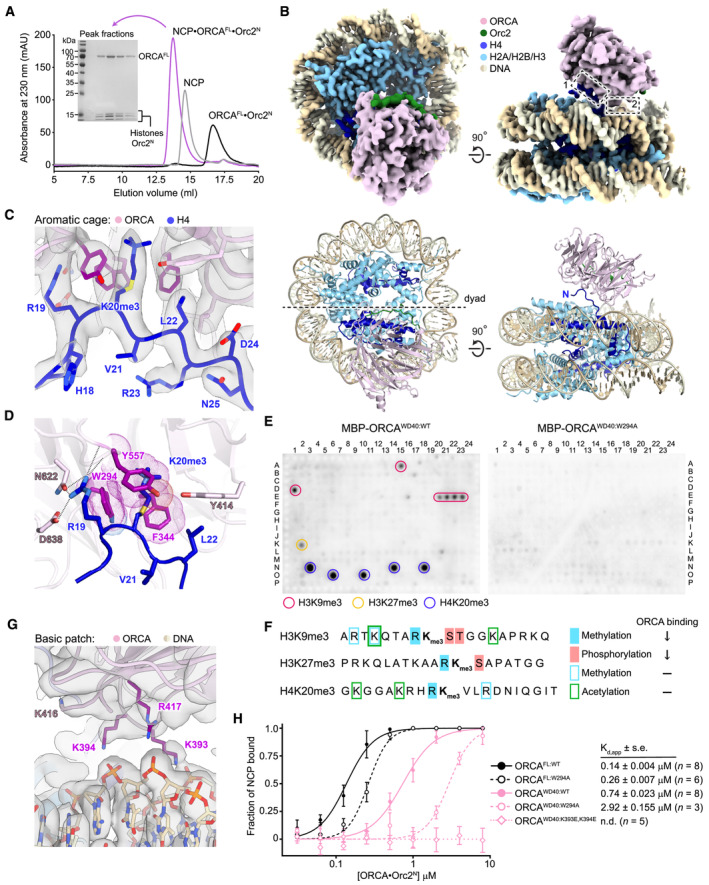
Figure 2. ORCA binds nucleosomes using both an aromatic cage and a basic surface patch in the WD40 β‐propeller.
-
APurification of the ORCAFL•Orc2N•H4K20me3‐nucleosome complex for cryo‐EM. Size exclusion chromatography of ORCAFL·Orc2N, H4K20me3‐nucleosomes (NCP), and the ORCAFL•Orc2N•H4K20me3‐nucleosome complex. Coomassie‐stained SDS–PAGE gel demonstrates coelution of histones and ORCA in peak fractions upon complex formation.
-
BCryo‐EM structure of the ORCAFL•Orc2N•H4K20me3‐nucleosome complex. Sharpened cryo‐EM map (top) and model (as cartoon, bottom) are shown. Dashed boxes mark interaction sites between ORCA and the H4K20me3‐nucleosome.
-
C, DORCA binds the H4K20me3‐modified H4 tail using an aromatic cage. Zoomed views of the H4‐tail‐binding site (interaction site 1 in B) are shown. (C) Sharpened cryo‐EM map of the H4•ORCA interface with H4 tail residues and interacting ORCA side chains in stick representation. (D) A rotated view of the H4•ORCA interface, emphasizing recognition of H4K20me3 by ORCA's aromatic cage (in purple) and hydrogen bonds or salt bridges (dashed lines) between H4‐R19 and ORCA.
-
E, FORCA binding to histone peptides containing repressive trimethylation marks requires an intact aromatic cage and unmodified neighboring histone tail residues. (E) Histone peptide arrays of wild‐type (ORCAWD40:WT) and aromatic cage‐mutant ORCA (ORCAWD40:W294A). (F) Summary of histone peptide array results for wild‐type ORCA and effects of combinatorial histone modifications on ORCA binding (↓ reduced binding; − binding unaltered).
-
GA basic patch in ORCA engages nucleosomal DNA (interaction site 2 in B). Sharpened cryo‐EM map with basic patch side chains shown as sticks. ORCA residues contacting nucleosomal DNA are colored purple.
-
HMutations in ORCA's aromatic cage and basic patch decrease ORCA's affinity for H4K20me3‐mononucleosomes. Binding curves (mean and s.d.) for wild‐type and mutant ORCA constructs measured by electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSAs) are shown. Apparent dissociation constants (Kd,app), standard error of mean (s.e.), and number of replicate experiments are listed. Representative EMSA gels are included in Appendix Fig S5. N.d., not determined.
Source data are available online for this figure.
