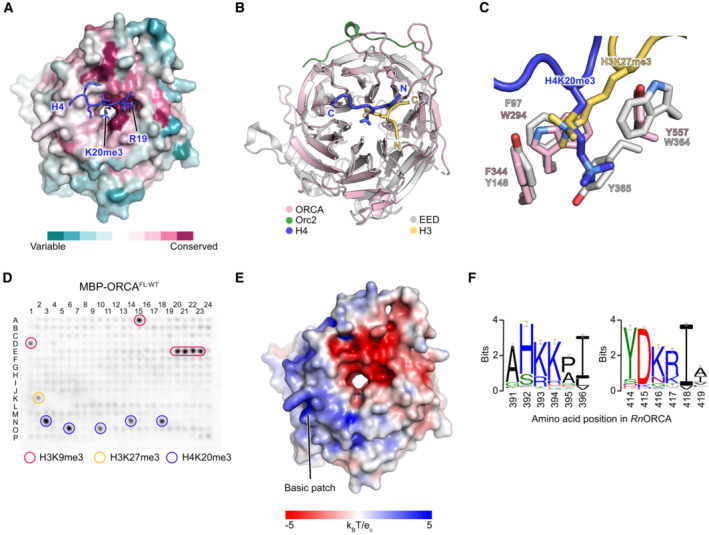
Figure EV2. ORCA binds nucleosomes using two surfaces on the WD40 domain.
-
AThe H4‐binding site constitutes a conserved region of the ORCA β‐propeller. The ORCAWD40 surface is colored according to ConSurf conservation scores.
-
B, CORCA's WD40 domain is structurally similar to that of EED. (B) Structural superposition of the WD40 domains of ORCA (this study) and EED (PDB 3IIW; Margueron et al, 2009) with bound H4 and H3 peptides, respectively. (C) Zoomed view of the aromatic cages in ORCA and EED.
-
DHistone peptide array binding experiment for full‐length (FL) ORCA. A similar set of modified histone peptides is bound by the full‐length protein as by the WD40 domain alone (compared to Fig 2E).
-
E, FPositively charged residues form a basic patch on the surface of ORCA's WD40 domain. (E) View of the nucleosome‐facing surface of ORCA's WD40 domain colored by electrostatic potential. (F) Sequence logo of DNA‐binding residues (K393, K394, and R417) in ORCA's basic patch reveals conservation of chemical side chain properties among ORCA orthologs.
