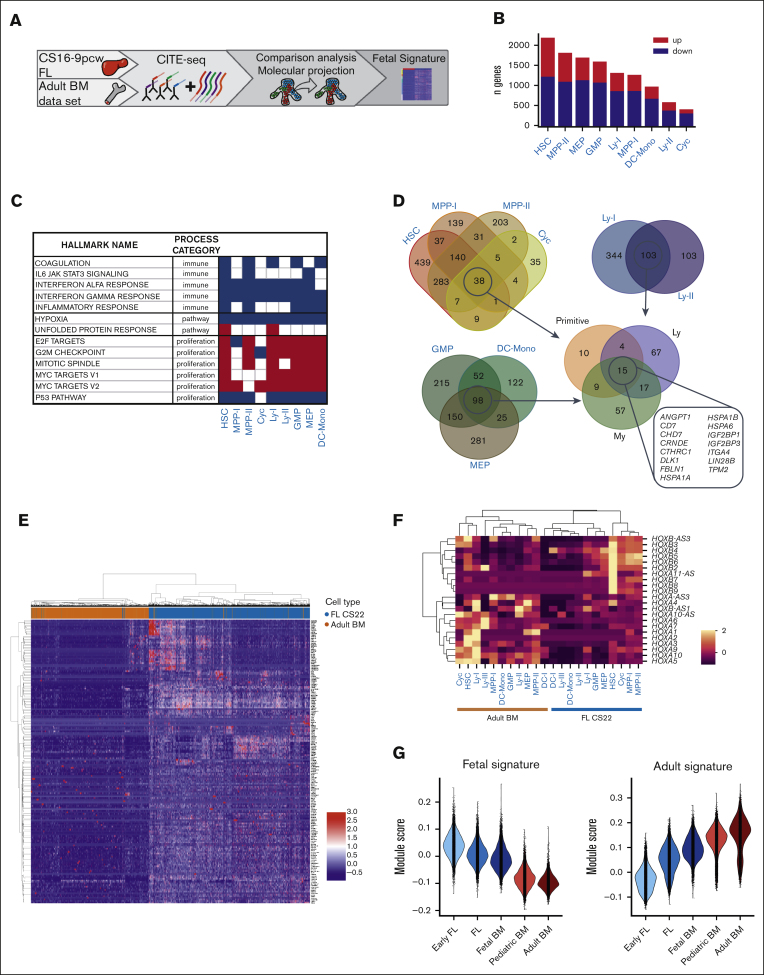
Figure 4.
Cluster-specific differential gene expression analysis defines a fetal–specific gene signature. (A) Schematic presentation of data in the figure. (B) Number of upregulated and downregulated genes in pseudobulked FL CS22 clusters compared with adult BM counterparts. Red bars; upregulated genes (fetal signature), blue bars; downregulated genes (adult signature), adj P value < .05. (C) GSEA of selected hallmark gene sets involved in immune processes, pathways, and proliferation; red; upregulated, blue; downregulated in FL according to NES value. False discovery rate q-value < 0.05. (D) Venn diagrams of upregulated genes in FL compared with adult BM defined by log2 fold change > 1 and adj P value < .05. (E) Heatmap showing expression of the fetal signature (primitive, My, Ly in Figure 4D) genes in FL CS22 (blue) and adult BM (brown), with cells displayed on the x-axis and genes on the y-axis. (F) Heatmap of mean HOX gene expression per cluster in FL CS22 and adult BM. (G) Module scores of the fetal (left) and adult (right) gene signature across development using data from an earlier study.6