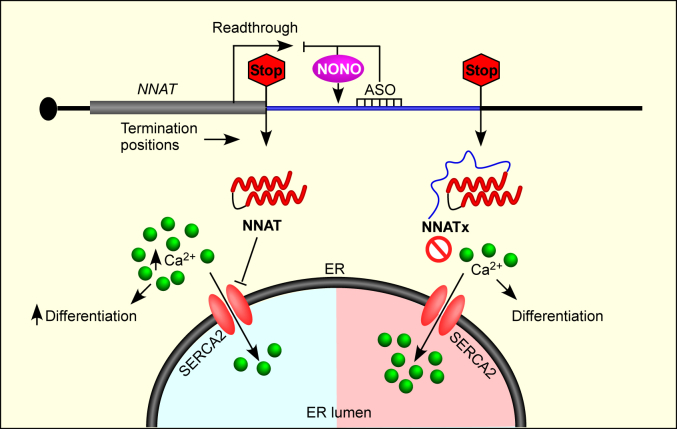
Figure 9.
The TCR of NNAT mRNA regulates cytoplasmic Ca2+level and neuronal differentiation.NNAT mRNA has two in-frame stop codons. Translation termination at the canonical stop codon generates NNAT isoform, which interacts with SERCA2 pump on the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane and inhibits its function. This increases cytoplasmic Ca2+ level promoting neuronal differentiation. TCR at the canonical stop codon and termination at the downstream in-frame stop codon results in a C-terminally extended isoform termed NNATx. This process is negatively regulated by the protein NONO. NNATx has a predicted intrinsically disordered region at the C-terminus and it does not interact with SERCA2. Therefore, it cannot increase the cytoplasmic Ca2+ level and does not promote neuronal differentiation, unlike NNAT. TCR of NNAT can be inhibited, and neuronal differentiation can be enhanced, by a synthetic antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) that targets the ISR of NNAT. ISR, inter stop codon region; SERCA2, sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase isoform 2; TCR, termination codon readthrough.