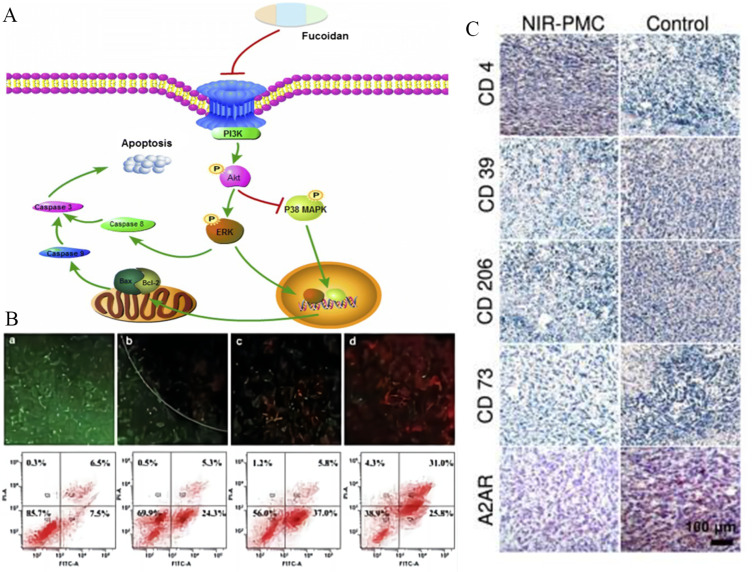
Figure 3.
Observations of the anticancer mechanism of algal extracts and their efficacy after treatment. (A) Molecular mechanism of the anticancer activity of algal extracts. Reprinted from Lin Y, Qi X, Liu H, et al. The anticancer effects of fucoidan: a review of both in vivo and in vitro investigations. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:154. Creative Commons.2 (B) Detection of apoptosis using live-dead cell cytostaining and flow cytometry. (a, AuNCs/HA upon NIR irradiation; b, DOX/AuNCs/HA; c, DOX/AuNCs/HA upon NIR irradiation; d, Reproduced with permission; doxorubicin (DOX); Gold nanorods (AuNRs); hyaluronic acid (HA)). Reprinted from Sun R, Chen H, Sutrisno L, et al. Nanomaterials and their composite scaffolds for photothermal therapy and tissue engineering applications. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2021;22(1):404–428. Creative Commons.56 (C) Representative images of tumor immunohistochemical staining. (near-infra-red (NIR), photosynthesis microcapsule (PMC)). Reprinted from Wang W, Zheng H, Jiang J, et al. Engineering micro oxygen factories to slow tumor progression via hyperoxic microenvironments. Nature communications. 2022;13(1):4495. Creative Commons.48