FIGURE 2.
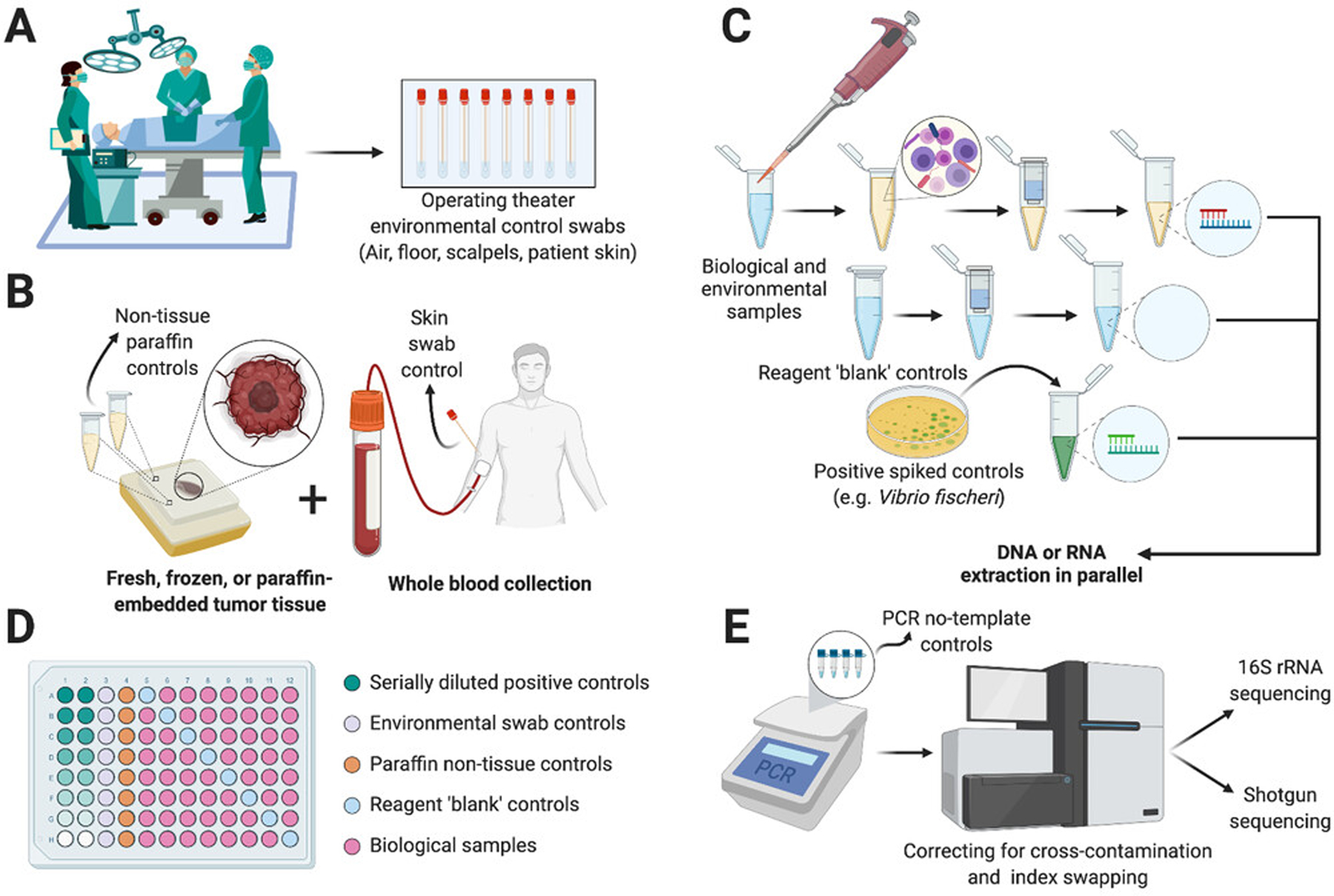
Extracting and analyzing low-biomass microbiomes requires special care to control external and internal contamination.[88,107,108] (A) Collection of environmental controls ideally begins in the operating room to account for non-patient environmental sources. (B) Post-operative tissues, if paraffin embedded, can have non-tissue paraffin controls taken to ensure the embedding process is not contaminated. Whole blood should ideally be collected with a skin swab to account for peri-needle contamination. (C) Negative reagent-only ‘blank’ controls and positive titrated controls should be processed simultaneously alongside nucleic acid extraction from biological and environmental samples. (D) Plating strategies should be considered to reduce cross-contamination; controls may include up to 40% of total samples. (E) Amplification steps may include PCR no-template controls and sequencing may include correction for cross-contamination or index swapping, although the latter remains challenging.
