Fig. 5. Functional validation of the RapaCasp9-G suicide gene in RapaCasp9-G-expressing GMTCs from HDs and AML patients in clinically relevant conditions.
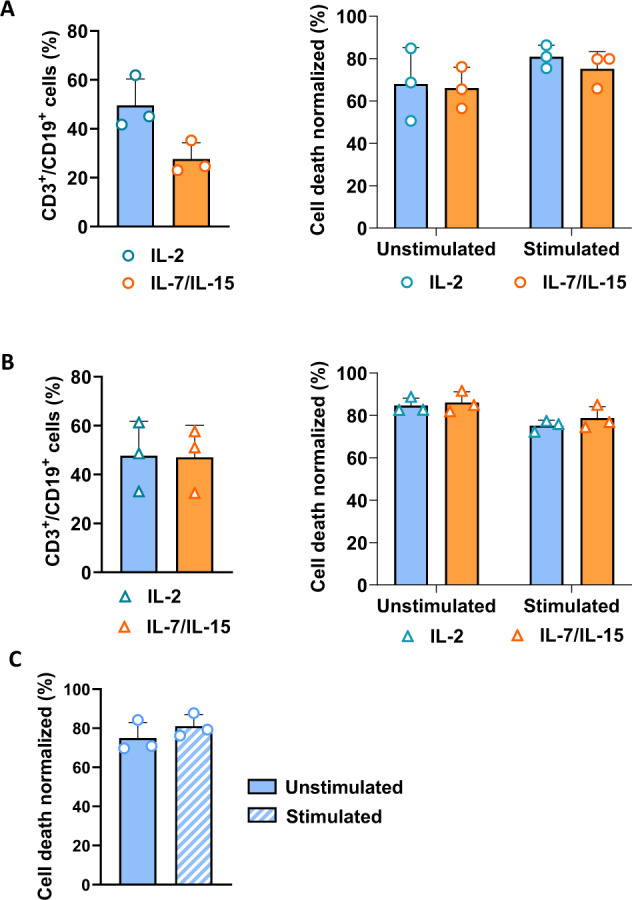
A Left, lentiviral transduction efficiency of T cells in IL-2 and IL-7/IL-15 conditions determined by flow cytometry. T cells from HDs were genetically modified. Transduction efficiency was analyzed on day 7 after the beginning of production. Mean ± SD of three independent experiments; right, cell death percentages of RapaCasp9-G-expressing GMTCs stimulated with plate-bound IL-1RAP or left unstimulated for 24 h; the percentages were measured 24 h after rapamycin exposure. T cells were cultured in RPMI medium supplemented with IL-2 or in TexMacs medium supplemented with IL-7/IL-15. Normalized to control cells (DMSO exposure). Mean ± SD of three independent experiments. B Left, lentiviral transduction efficiency of T cells in IL-2 or IL-7/IL-15 conditions determined by flow cytometry. T cells from AML patients were genetically modified. Transduction efficiency was analyzed on day 7 after the beginning of production. Mean ± SD of three independent experiments; right, cell death percentages of RapaCasp9-G-expressing cells stimulated with plate-bound IL-1RAP or left unstimulated for 24 h prior to culture in IL-2 or IL-7/IL-15 conditions; the percentages were measured 24 h after rapamycin exposure. Normalization to control cells (DMSO exposure). Mean ± SD of three independent experiments. C Cell death percentages of freshly thawed RapaCasp9-G-expressing GMTCs stimulated with plate-bound IL-1RAP-coated or left unstimulated for 24 h; the percentages were measured 24 h after rapamycin exposure. Normalized to control cells (DMSO exposure). Mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
