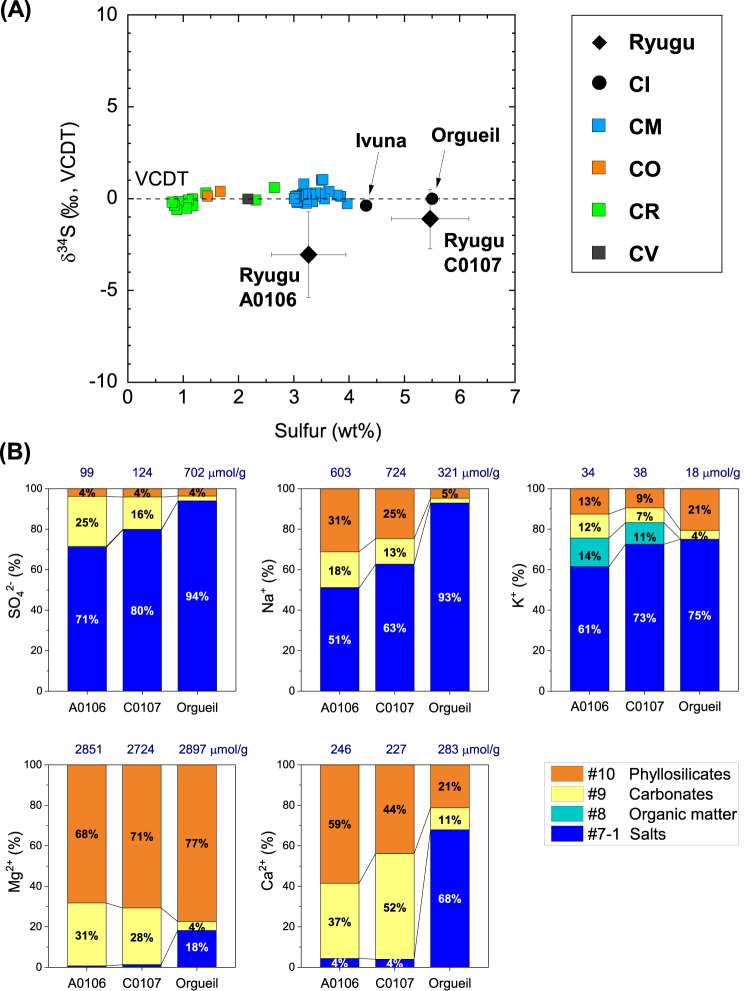
Fig. 1. Element compositions of the Ryugu samples.
A Total sulfur content (wt%) and isotopic profiles of the Ryugu samples (A0106, C0107) and of representative carbonaceous groups (CI, CM, CO, CR, and CV). Sulfur (S, wt%) and δ34S (‰ vs. VCDT) values are from the literature4, 17, 47 and references therein. Error bars are one standard deviation (1 SD) values of multiple particles. B Relative amounts of sulfate, sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium in sequential solvent extracts of the samples collected at the first touchdown site (A0106) and the second touchdown site (C0107) on the asteroid Ryugu (Supplementary Fig. 1), and in a sample from Orgueil (values less than 3% were omitted). C0107 may contain subsurface samples from ejecta associated with the artificially made impact crater. We used fine-grained samples and carried out the sequential solvent extraction in a clean room4 (Supplementary Fig. 1). We measured evaporitic salts (via #7-1 hot water extraction, see IDs in Supplementary Fig. 1 and Naraoka et al.4); ions bound to soluble organic matter (via #8 dichloromethane and methanol, DCM+MeOH); exchangeable ions and highly soluble minerals such as carbonates (via #9 formic acid, HCOOH); and clays and residual soluble minerals (via #10 hydrochloric acid, HCl). Navy numbers are the sum of extractable solute contents for each solute. Data are provided as a Source Data file.