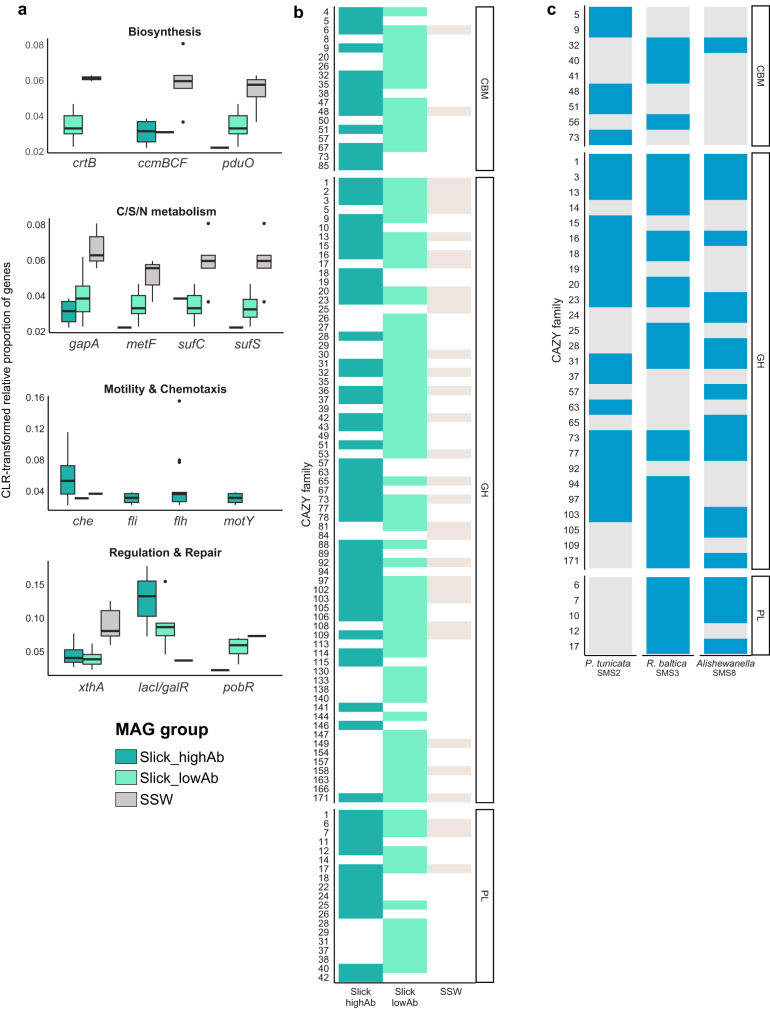
Fig. 4. Relative fraction of genes from specific functional pathways with differential abundance between MAG groups, identified using ALDEx2 and displayed as CLR-transformed relative gene abundances.
Several genes from functionally related categories (e.g. che chemotaxis, fli/flh flagellum genes) were combined, showing the average CLR value. lacI/galR LacI family transcriptional regulator, xthA exodeoxyribonuclease, motY sodium−type flagellar protein, pobR AraC family transcriptional regulator, sufS cysteine desulfurase/selenocysteine lyase, sufC Fe − S cluster assembly ATP-binding protein, metF methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase, gapA glyceraldehyde 3−phosphate dehydrogenase, pduO cob(I)alamin adenosyltransferase, crtB 15−cis−phytoene synthase, ccmBCF cytochrome/heme biogenesis/transport (Table S4c) (a). Diversity of CAZyme families in different MAG groups (see Table S4d for details) (b). CAZyme profiles of slick SML isolates, showing presence/absence of carbohydrate-binding module (CBM), glycoside hydrolase (GH), and polysaccharide lyase (PL) gene families (Table S2e). The four R. baltica isolates featured identical CAZyme diversity; therefore, only SMS3 is shown as representative. Due to lower completeness of SMS9, only SMS8 is shown for Alishewanella sp. (c).