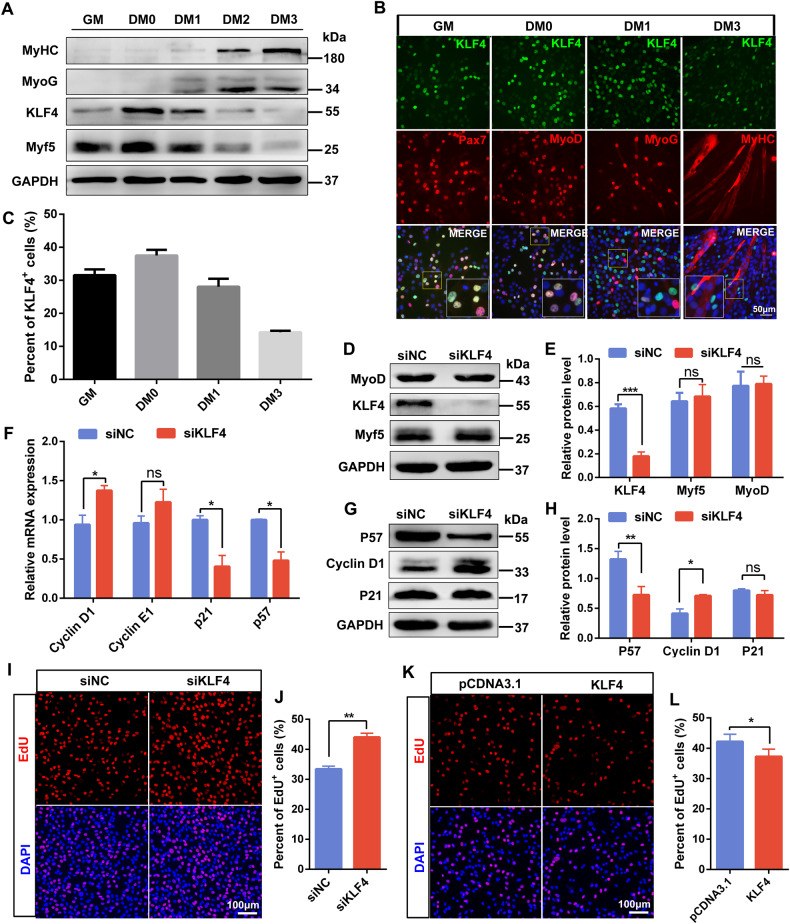
Fig. 5. KLF4 inhibits myoblast proliferation.
A WB analyses of KLF4 and myogenic markers protein expression were performed in C2C12 cells grown in growth medium (GM), as well as in differentiation medium (DM) for 0d, 1d, 2d, and 3d (DM 0-3). GAPDH was used as a loading control. B Immunofluorescence staining of KLF4 and myogenic markers in C2C12 cells at several indicated time points. Scale bar = 50 μm. C The percentages of KLF4+ cells compared with the total number of nuclei in (B) were presented (n = 3, each). D Western blot analyzed the protein levels of KLF4 and two myogenic transcription factors (MyoD and Myf5) in C2C12 cells transfected with negative control siRNAs (siNC) or KLF4 siRNAs (siKLF4). E The relative protein levels of target proteins normalized to GAPDH signals in (D) were obtained through WB band grey scanning (n = 3). F qPCR detection of KLF4 and cell cycle-related gene expression in C2C12 cells described as (D) (n = 3). G. WB analyzed the protein levels of KLF4 and cell cycle-related gene expression. H The relative protein levels of target proteins normalized to GAPDH signals in (G) were obtained through WB band grey scanning (n = 3). I Representative images of the EdU staining for si-KLF4 C2C12 cells. Scale bar = 100 μm. J The percentages of EdU-positive cells compared with the total number of nuclei were presented (n = 3). K. EdU staining for C2C12 cells after KLF4 overexpression. Scale bar = 100 μm. L The percentages of EdU-positive cells in (K) were counted (n = 3). Data are represented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (Student’s t test).