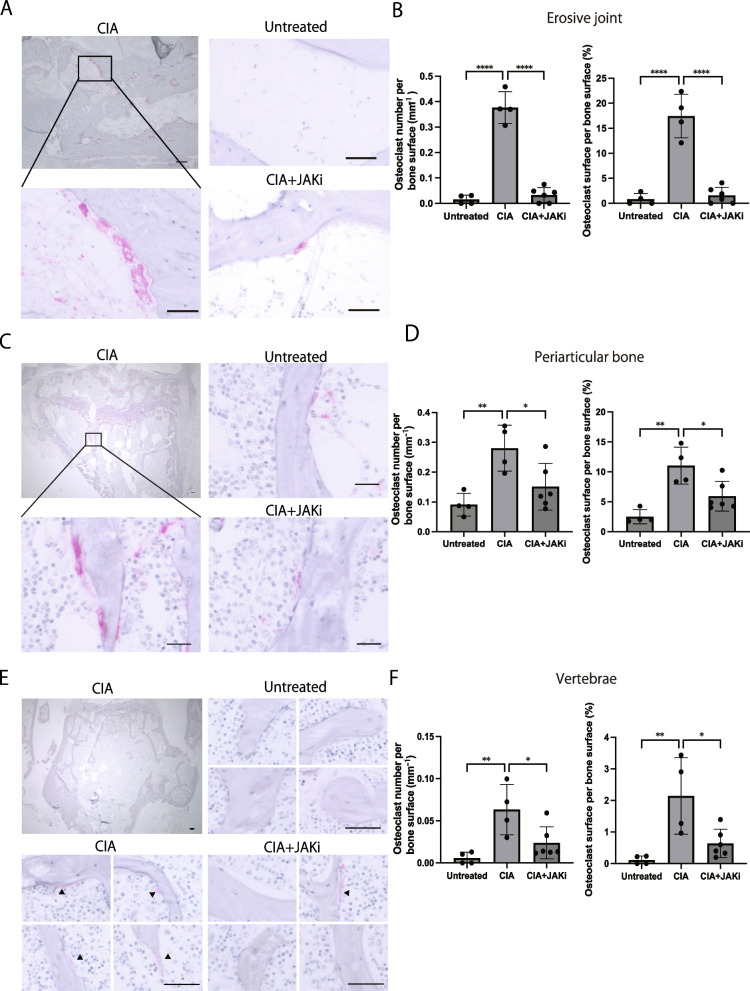
Fig. 2.
The effect of the JAK inhibitor on osteoclastogenic bone resorption in the three different types of bone damage in autoimmune arthritis. A, B Representative TRAP+ staining (A) and the number of TRAP+ multinucleated cells per bone surface (B) of the calcaneocuboid joint of untreated (n = 4), CIA (n = 4), and CIA + JAKi mice (n = 6). C, D Representative TRAP+ staining (C) and the number of TRAP+ multinucleated cells per bone surface (D) of periarticular bone (proximal tibia) of untreated (n = 4), CIA (n = 4) and CIA + JAKi mice (n = 6). E, F Representative TRAP+ staining (E) and the number of TRAP+ multinucleated cells per bone surface (F) of lumbar vertebrae of untreated (n = 4), CIA (n = 4), and CIA + JAKi mice (n = 6). Scale bar: (100 μm, upper left; 50 μm, others) (A, E). (100 μm, upper left; 25 μm, others) (C). All data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; by one-way ANOVA with the Holm-Sidak multiple comparisons test (B, D, F)