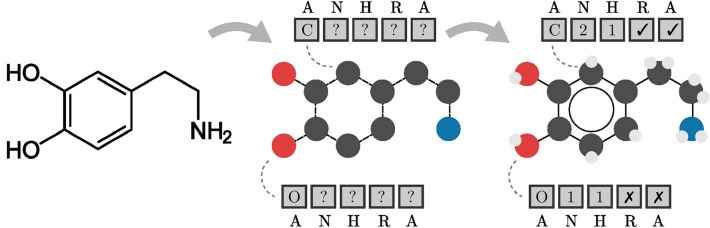
Fig. 1.
The information gain from using atomic features. Compound structure (left) can be encoded as a molecular graph in which atoms are nodes and bonds are edges. Atomic features are assigned to each node, and at least atom types (A) are required to identify atoms (middle). Bond identification (e.g. bond order) can be implicitly encoded in atomic features by providing information about the number of heavy neighbors (N) and implicit hydrogens (H). Other features such as inclusion in rings (R) or aromatic rings (A) can help graph models in finding relevant patterns (right)