Figure 3: Increasing Cx36 gap junction coupling protects against islet dysfunction and cell death.
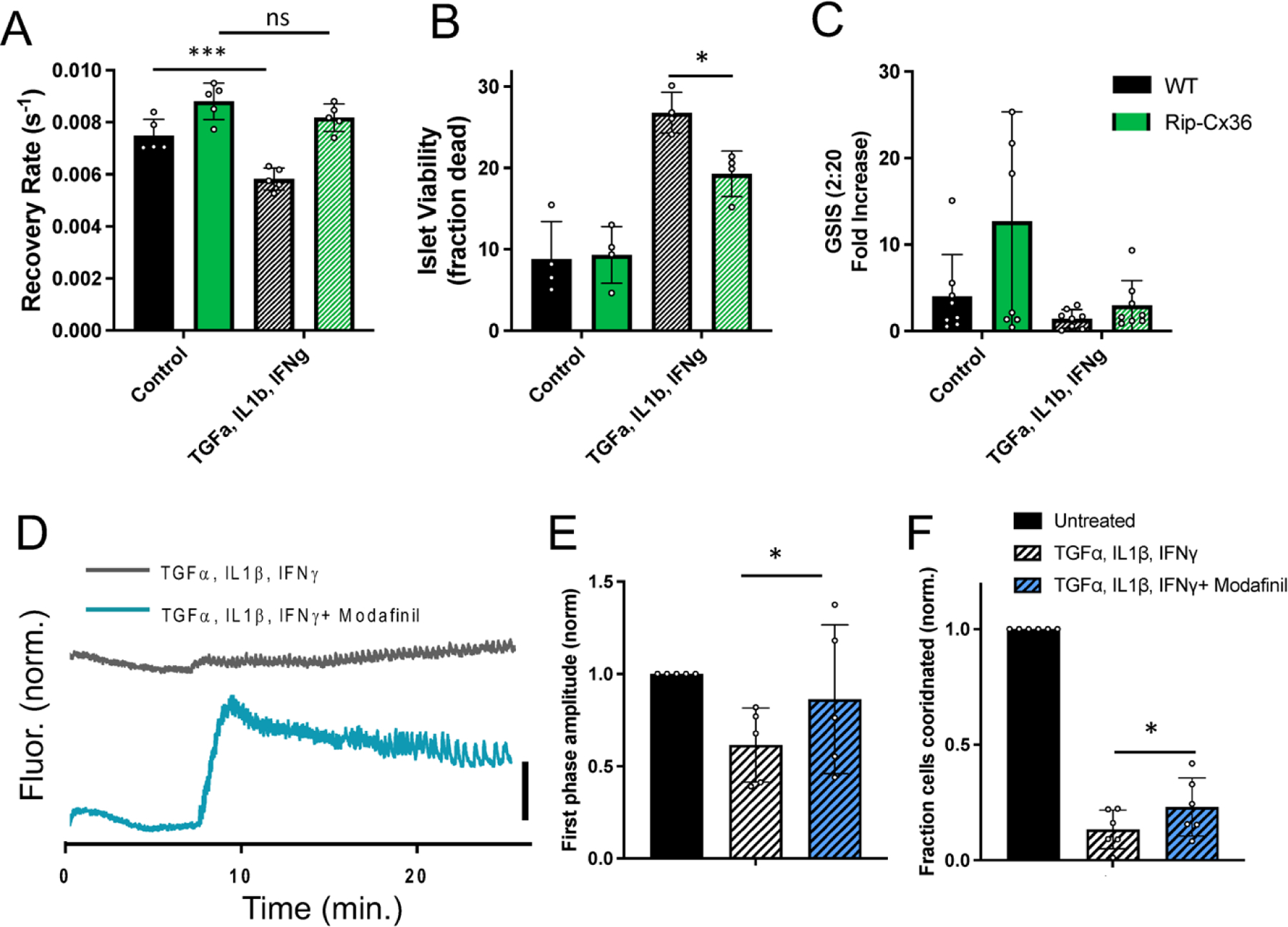
A) Mean gap junction permeability, as measured by FRAP recovery rate, in islets from wild-type and Rip-Cx36 overexpression mice, that are either untreated or treated with a cocktail of 1 ng/ml mouse recombinant TNF-α, 0.5 ng/ml IL-1β, 10 ng/ml IFN-γ. B) Islet viability, as indicated by the proportion of cells labelled as dead, in islets as in A. C) Glucose-stimulated Insulin secretion (GSIS) in islets as in A. D) Representative [Ca2+] time courses averaged over an islet treated with TNF-α, IL-1β, IFN-γ as in A-C (grey) or an islet treated with TNF-α, IL-1β, IFN-γ as in A-C plus 50 μM modafinil. E) Amplitude of [Ca2+] elevation ~10 minutes after glucose elevation, for untreated islets and treatments in D. Data is normalized to the elevation measured in untreated islets. F) Area of coordinated [Ca2+] normalized to islet size (fraction coordinated), for untreated islets and treatments in D. Data is normalized to the elevation measured in untreated islets. Data in A representative of n=5 wild-type and n=5 Rip-Cx36 mice; data in B representative of n=4 wild-type and n=4 Rip-Cx36 mice; data in C representative of n=8 wild-type and n=8 Rip-Cx36 mice; data in E representative of n=5 mice for each treatment, data in F representative of n=6 mice for each treatment. In A * represents p=0.0007, ns represents p=0.21; in B * represents p=0.02; in E * represents p=0.04; in B * represents p=0.05; comparing groups indicated (all unpaired Student’s t-test). Data in A-C, E-F presented as mean±S.D. with each data point representing an islet (A,B,E,F) or independent experiment (C).
