Figure 7: Optogenetic D1 receptor activation in dCA1 rescues linking deficits caused by LC to dCA1 inhibition.
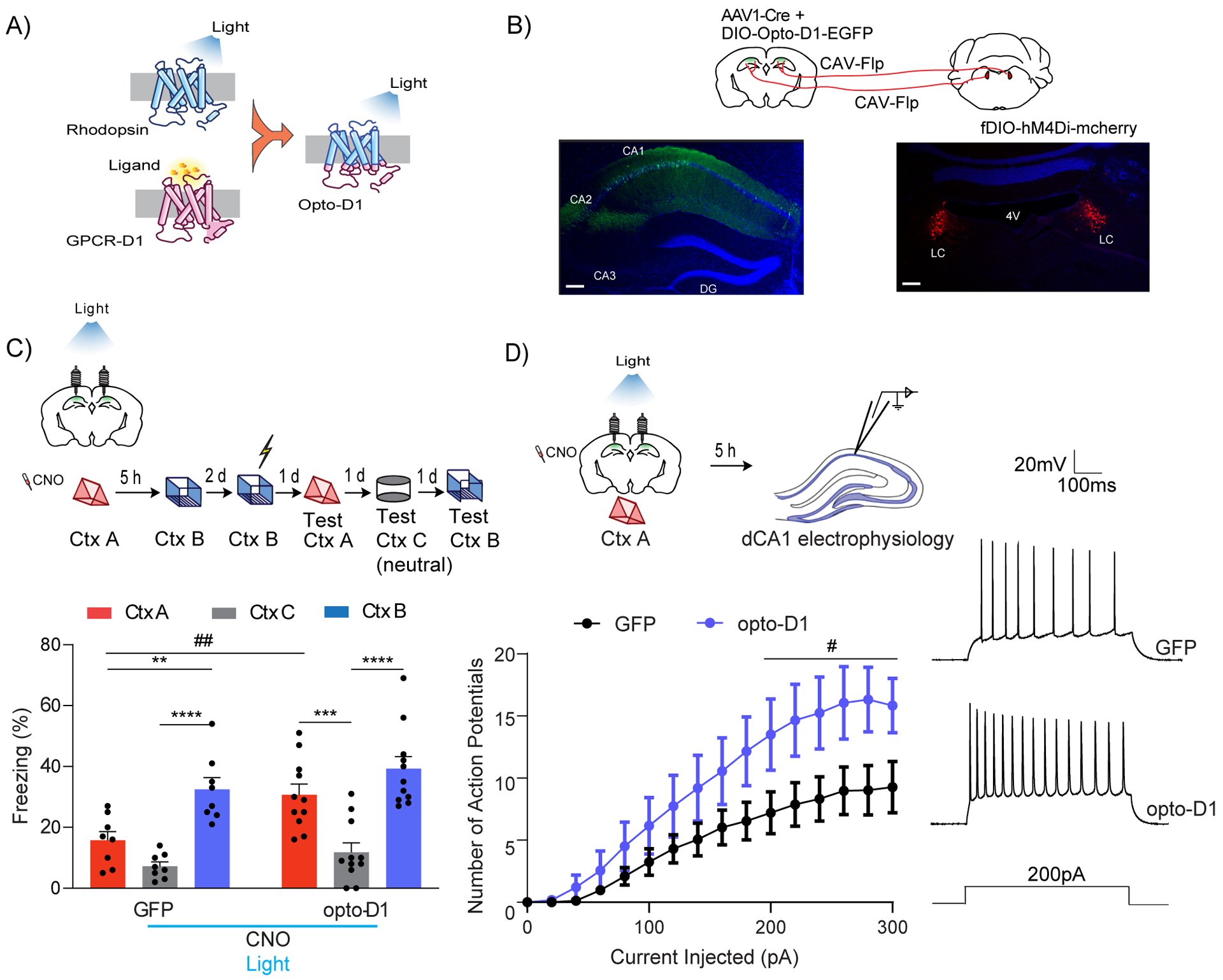
(A) Schematics of the Opto-D1 construct.
(B) Schematics of experimental design. Scale bars, 300μm.
(C) Optogenetic activation of D1 receptor signaling in a fraction of all cell types in dCA1 rescued the contextual memory linking deficit caused by chemogenetic inhibition of LC cells projecting to dCA1. (GFP, n=8; opto-D1, n=11; two-way repeated measures ANOVA, Sidak post hoc,*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, ##p<0.01). * is used to depict significance within groups and # is used to show significance between groups for two-way RM ANOVA. Clozapine-N-oxide and light were given to all mice.
(D) Optogenetic activation of the D1 receptor during context exploration rescued the reduction in dCA1 firing rate caused by chemogenetic inhibition of LC cells projecting to the dCA1. (GFP, n=11; opto-D1, n=10; two-way repeated measures ANOVA, factor: D1 activation F(1,19) = 4.50, #p<0.05). Clozapine-N-oxide and light were given to all mice.
All results are mean + s.e.m.
