Figure 5.
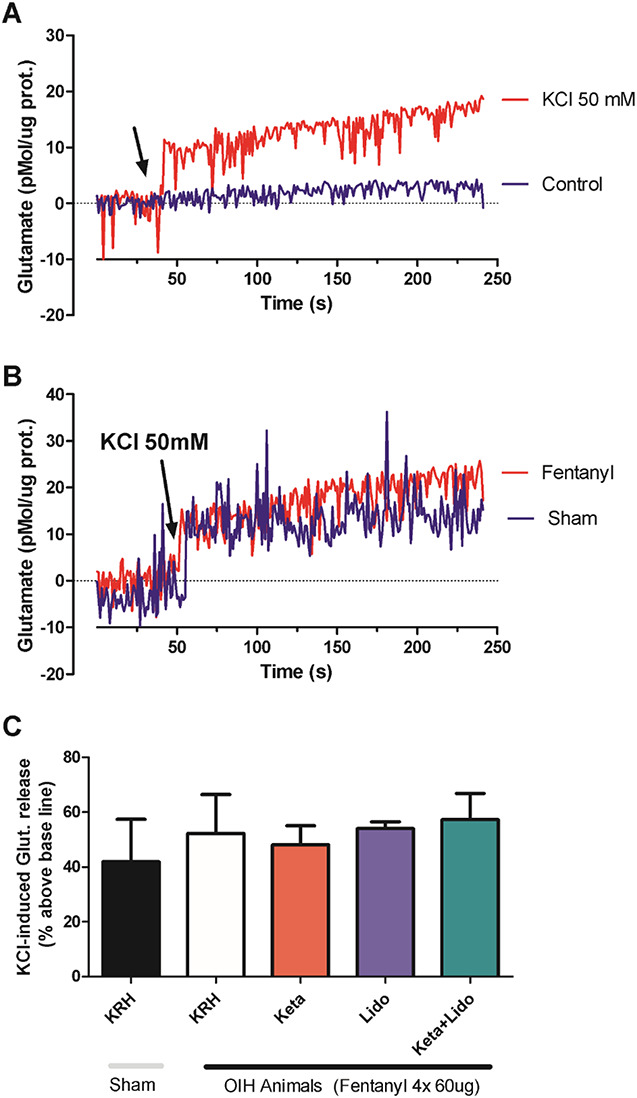
Absence of effect of OIH and treatments on glutamate release in spinal cord synaptosomes. (A) Glutamate levels are expressed as a function of time. The arrow indicates the timing of the addition of 50 mM potassium chloride (KCl) to the synaptosomal preparation (red line) or the addition of the corresponding volume of physiological solution (krebs Ringer hepes or physiological solution [KRH], blue line). The KCl-mediated depolarizing stimulus triggers glutamate release from synaptosomes indicated by increased fluorescence levels. (B) KCl-induced depolarization triggers a similar elevation in glutamate levels in synaptosomes from animals previously treated with physiological solution (sham group, blue line) or animals treated with 4 doses of 60 µg fentanyl (fentanyl group, red line). (C) Quantification, in bars, of the KCl-induced glutamate elevation in the different experimental conditions as indicated. Incubation with ketamine, lidocaine, or ketamine + lidocaine was performed directly on the synaptosomal preparation 5 minutes before the addition of KCl. (N = 5 independent experiments; P > 0.05 1-way ANOVA). ANOVA, analysis of variance; OIH, opioid-induced hyperalgesia.
