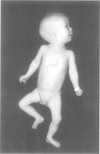
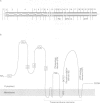
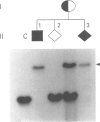
Full text
PDF

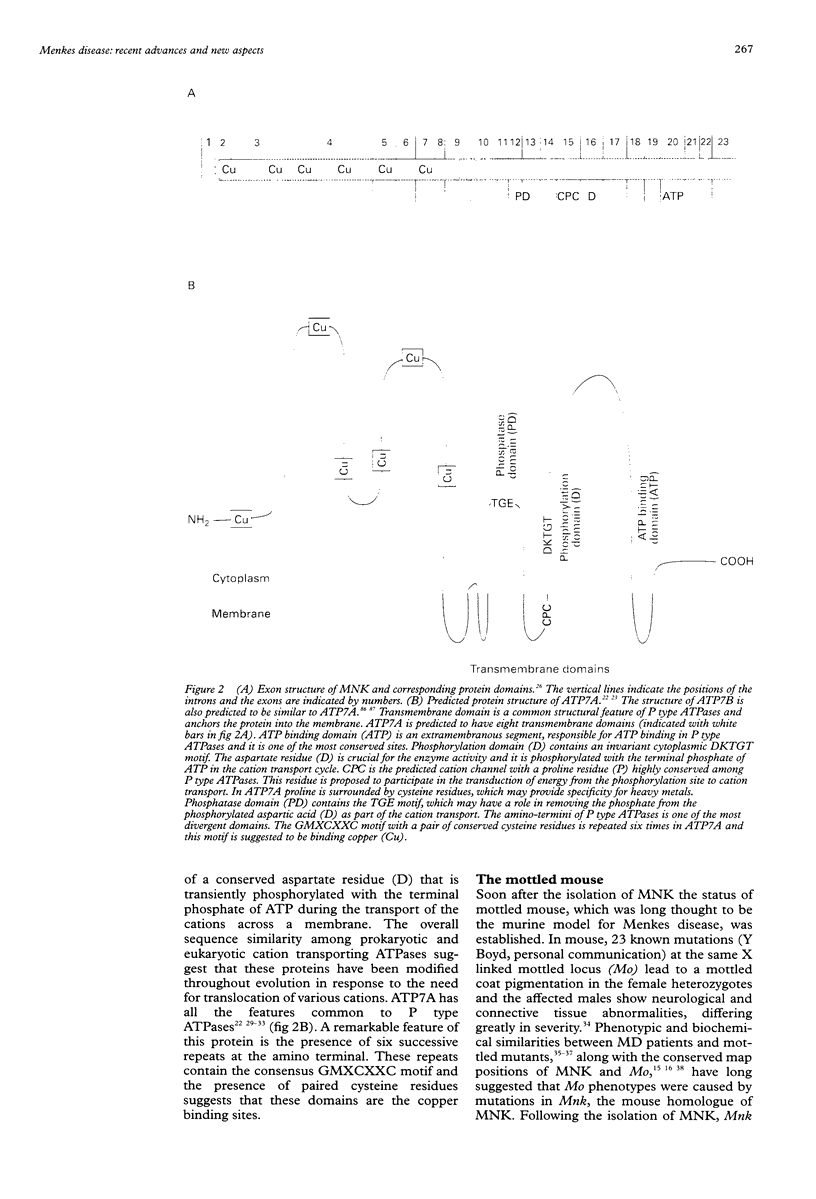







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck J., Enders H., Schliephacke M., Buchwald-Saal M., Tümer Z. X;1 translocation in a female Menkes patient: characterization by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Clin Genet. 1994 Oct;46(4):295–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1994.tb04163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begy C. R., Dierick H. A., Innis J. W., Glover T. W. Two highly polymorphic CA repeats in the Menkes gene (ATP7A). Hum Genet. 1995 Sep;96(3):355–356. doi: 10.1007/BF00210423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowcock A. M., Farrer L. A., Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Hebert J. M., Kidd K. K., Frydman M., Bonne-Tamir B. Mapping the Wilson disease locus to a cluster of linked polymorphic markers on chromosome 13. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Jul;41(1):27–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowcock A. M., Farrer L. A., Hebert J. M., Agger M., Sternlieb I., Scheinberg I. H., Buys C. H., Scheffer H., Frydman M., Chajek-Saul T. Eight closely linked loci place the Wilson disease locus within 13q14-q21. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):664–674. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G. J., Yuzbasiyan-Gurkan V. Wilson disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 1992 May;71(3):139–164. doi: 10.1097/00005792-199205000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockdorff N., Kay G., Smith S., Keer J. T., Hamvas R. M., Brown S. D., Rastan S. High-density molecular map of the central span of the mouse X chromosome. Genomics. 1991 May;10(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90478-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull P. C., Cox D. W. Wilson disease and Menkes disease: new handles on heavy-metal transport. Trends Genet. 1994 Jul;10(7):246–252. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull P. C., Thomas G. R., Rommens J. M., Forbes J. R., Cox D. W. The Wilson disease gene is a putative copper transporting P-type ATPase similar to the Menkes gene. Nat Genet. 1993 Dec;5(4):327–337. doi: 10.1038/ng1293-327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelly J., Tümer Z., Tønnesen T., Petterson A., Ishikawa-Brush Y., Tommerup N., Horn N., Monaco A. P. Isolation of a candidate gene for Menkes disease that encodes a potential heavy metal binding protein. Nat Genet. 1993 Jan;3(1):14–19. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. W. Genes of the copper pathway. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Apr;56(4):828–834. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danks D. M., Campbell P. E., Walker-Smith J., Stevens B. J., Gillespie J. M., Blomfield J., Turner B. Menkes' kinky-hair syndrome. Lancet. 1972 May 20;1(7760):1100–1102. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91433-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danks D. M. Of mice and men, metals and mutations. J Med Genet. 1986 Apr;23(2):99–106. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.2.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danks D. M. The mild form of Menkes disease: progress report on the original case. Am J Med Genet. 1988 Jul;30(3):859–864. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das S., Levinson B., Vulpe C., Whitney S., Gitschier J., Packman S. Similar splicing mutations of the Menkes/mottled copper-transporting ATPase gene in occipital horn syndrome and the blotchy mouse. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Mar;56(3):570–576. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das S., Levinson B., Whitney S., Vulpe C., Packman S., Gitschier J. Diverse mutations in patients with Menkes disease often lead to exon skipping. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Nov;55(5):883–889. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das S., Whitney S., Taylor J., Chen E., Levinson B., Vulpe C., Gitschier J., Packman S. Prenatal diagnosis of Menkes disease by mutation analysis. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1995;18(3):364–365. doi: 10.1007/BF00710435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davisson M. T. X-linked genetic homologies between mouse and man. Genomics. 1987 Nov;1(3):213–227. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90047-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrer L. A., Bowcock A. M., Hebert J. M., Bonné-Tamir B., Sternlieb I., Giagheddu M., St George-Hyslop P., Frydman M., Lössner J., Demelia L. Predictive testing for Wilson's disease using tightly linked and flanking DNA markers. Neurology. 1991 Jul;41(7):992–999. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.7.992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydman M., Bonné-Tamir B., Farrer L. A., Conneally P. M., Magazanik A., Ashbel S., Goldwitch Z. Assignment of the gene for Wilson disease to chromosome 13: linkage to the esterase D locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1819–1821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes A. M., Tønnesen T., Horn N., Grisar T., Marg W., Müller A., Reinsch R., Barton N. W., Guiraud P., Joannard A. Clinical expression of Menkes syndrome in females. Clin Genet. 1990 Dec;38(6):452–459. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1990.tb03612.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkin R. I., Schulman J. D., Schulman C. B., Bronzert D. A. Changes in total, nondiffusible, and diffusible plasma zinc and copper during infancy. J Pediatr. 1973 May;82(5):831–837. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herd S. M., Camakaris J., Christofferson R., Wookey P., Danks D. M. Uptake and efflux of copper-64 in Menkes'-disease and normal continuous lymphoid cell lines. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 15;247(2):341–347. doi: 10.1042/bj2470341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn N., Heydorn K., Damsgaard E., Tygstrup I., Vestermark S. Is Menkes syndrome a copper storage disorder? Clin Genet. 1978 Sep;14(3):186–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1978.tb02128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn N. Menkes X linked disease: heterozygous phenotype in uncloned fibroblast cultures. J Med Genet. 1980 Aug;17(4):257–261. doi: 10.1136/jmg.17.4.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn N. Menkes' X-linked disease: prenatal diagnosis and carrier detection. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1983;6 (Suppl 1):59–62. doi: 10.1007/BF01811325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn N., Mooy P., McGuire V. M. Menkes X linked disease: two clonal cell populations in heterozygotes. J Med Genet. 1980 Aug;17(4):262–266. doi: 10.1136/jmg.17.4.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn N., Stene J., Møllekaer A. M., Friedrich U. Linkage studies in Menkes' disease. The Xg blood group system and C-banding of the X chromosome. Ann Hum Genet. 1984 May;48(Pt 2):161–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1984.tb01011.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn N., Tønnesen T., Tümer Z. Menkes disease: an X-linked neurological disorder of the copper metabolism. Brain Pathol. 1992 Oct;2(4):351–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1992.tb00711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houwen R. H., Juyn J., Hoogenraad T. U., Ploos van Amstel J. K., Berger R. H714Q mutation in Wilson disease is associated with late, neurological presentation. J Med Genet. 1995 Jun;32(6):480–482. doi: 10.1136/jmg.32.6.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. M. Primary defect in copper transport underlies mottled mutants in the mouse. Nature. 1974 Jun 28;249(460):852–854. doi: 10.1038/249852a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hämäläinen E. R., Jones T. A., Sheer D., Taskinen K., Pihlajaniemi T., Kivirikko K. I. Molecular cloning of human lysyl oxidase and assignment of the gene to chromosome 5q23.3-31.2. Genomics. 1991 Nov;11(3):508–516. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90057-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inesi G., Kirtley M. R. Structural features of cation transport ATPases. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992 Jun;24(3):271–283. doi: 10.1007/BF00768848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaler S. G., Gallo L. K., Proud V. K., Percy A. K., Mark Y., Segal N. A., Goldstein D. S., Holmes C. S., Gahl W. A. Occipital horn syndrome and a mild Menkes phenotype associated with splice site mutations at the MNK locus. Nat Genet. 1994 Oct;8(2):195–202. doi: 10.1038/ng1094-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaler S. G. Menkes disease. Adv Pediatr. 1994;41:263–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapur S., Higgins J. V., Delp K., Rogers B. Menkes syndrome in a girl with X-autosome translocation. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Feb;26(2):503–510. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320260230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keydorn K., Damsgaard E., Horn N., Mikkelsen M., Tygstrup I., Vestemark S., Weber J. Extra-hepatic storage of copper: a male foetus suspected of Menkes' disease. Humangenetik. 1975 Sep 10;29(2):171–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00430357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollros P. R., Dick R. D., Brewer G. J. Correction of cerebrospinal fluid copper in Menkes kinky hair disease. Pediatr Neurol. 1991 Jul-Aug;7(4):305–307. doi: 10.1016/0887-8994(91)90052-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuder J., Otten A., Fuder H., Tümer Z., Tønnesen T., Horn N., Dralle D. Clinical and biochemical consequences of copper-histidine therapy in Menkes disease. Eur J Pediatr. 1993 Oct;152(10):828–832. doi: 10.1007/BF02073380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson B., Gitschier J., Vulpe C., Whitney S., Yang S., Packman S. Are X-linked cutis laxa and Menkes disease allelic? Nat Genet. 1993 Jan;3(1):6–6. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Togashi Y., Sato S., Emoto T., Kang J. H., Takeichi N., Kobayashi H., Kojima Y., Une Y., Uchino J. Spontaneous hepatic copper accumulation in Long-Evans Cinnamon rats with hereditary hepatitis. A model of Wilson's disease. J Clin Invest. 1991 May;87(5):1858–1861. doi: 10.1172/JCI115208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MENKES J. H., ALTER M., STEIGLEDER G. K., WEAKLEY D. R., SUNG J. H. A sex-linked recessive disorder with retardation of growth, peculiar hair, and focal cerebral and cerebellar degeneration. Pediatrics. 1962 May;29:764–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara O., Takaoka H., Nasu M., Iwakawa Y., Okeda R. An autopsy case of Menkes kinky hair disease. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1978 Jul;28(4):585–594. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1978.tb00897.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer J. F., Grimes A., Ambrosini L., Lockhart P., Paynter J. A., Dierick H., Glover T. W. Mutations in the murine homologue of the Menkes gene in dappled and blotchy mice. Nat Genet. 1994 Apr;6(4):374–378. doi: 10.1038/ng0494-374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer J. F., Livingston J., Hall B., Paynter J. A., Begy C., Chandrasekharappa S., Lockhart P., Grimes A., Bhave M., Siemieniak D. Isolation of a partial candidate gene for Menkes disease by positional cloning. Nat Genet. 1993 Jan;3(1):20–25. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadal D., Baerlocher K. Menkes' disease: long-term treatment with copper and D-penicillamine. Eur J Pediatr. 1988 Aug;147(6):621–625. doi: 10.1007/BF00442477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. T., Chapman V. M. Electrophoretic variation for x-chromosome-linked phosphoglycerate kinase (pgk-1) in the mouse. Genetics. 1977 Oct;87(2):319–325. doi: 10.1093/genetics/87.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odermatt A., Suter H., Krapf R., Solioz M. Primary structure of two P-type ATPases involved in copper homeostasis in Enterococcus hirae. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12775–12779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltonen L., Kuivaniemi H., Palotie A., Horn N., Kaitila I., Kivirikko K. I. Alterations in copper and collagen metabolism in the Menkes syndrome and a new subtype of the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Biochemistry. 1983 Dec 20;22(26):6156–6163. doi: 10.1021/bi00295a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrukhin K., Lutsenko S., Chernov I., Ross B. M., Kaplan J. H., Gilliam T. C. Characterization of the Wilson disease gene encoding a P-type copper transporting ATPase: genomic organization, alternative splicing, and structure/function predictions. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Sep;3(9):1647–1656. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.9.1647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phung L. T., Ajlani G., Haselkorn R. P-type ATPase from the cyanobacterium Synechococcus 7942 related to the human Menkes and Wilson disease gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 27;91(20):9651–9654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.20.9651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rad M. R., Kirchrath L., Hollenberg C. P. A putative P-type Cu(2+)-transporting ATPase gene on chromosome II of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1994 Sep;10(9):1217–1225. doi: 10.1002/yea.320100910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. W., McGoodwin E. B., Martin G. R., Grahn D. Decreased lysyl oxidase activity in the aneurysm-prone, mottled mouse. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):939–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royce P. M., Camakaris J., Danks D. M. Reduced lysyl oxidase activity in skin fibroblasts from patients with Menkes' syndrome. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 15;192(2):579–586. doi: 10.1042/bj1920579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar B., Lingertat-Walsh K., Clarke J. T. Copper-histidine therapy for Menkes disease. J Pediatr. 1993 Nov;123(5):828–830. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)80870-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R. Structure and function of proton translocating ATPase in plasma membranes of plants and fungi. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 24;947(1):1–28. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood G., Sarkar B., Kortsak A. S. Copper histidinate therapy in Menkes' disease: prevention of progressive neurodegeneration. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1989;12 (Suppl 2):393–396. doi: 10.1007/BF03335432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Nucifora G., Phung L. T. Human Menkes X-chromosome disease and the staphylococcal cadmium-resistance ATPase: a remarkable similarity in protein sequences. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Oct;10(1):7–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00898.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Petrukhin K., Chernov I., Pellequer J. L., Wasco W., Ross B., Romano D. M., Parano E., Pavone L., Brzustowicz L. M. The Wilson disease gene is a copper transporting ATPase with homology to the Menkes disease gene. Nat Genet. 1993 Dec;5(4):344–350. doi: 10.1038/ng1293-344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. R., Forbes J. R., Roberts E. A., Walshe J. M., Cox D. W. The Wilson disease gene: spectrum of mutations and their consequences. Nat Genet. 1995 Feb;9(2):210–217. doi: 10.1038/ng0295-210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. R., Jensson O., Gudmundsson G., Thorsteinsson L., Cox D. W. Wilson disease in Iceland: a clinical and genetic study. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 May;56(5):1140–1146. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. R., Roberts E. A., Walshe J. M., Cox D. W. Haplotypes and mutations in Wilson disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jun;56(6):1315–1319. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommerup N., Tümer Z., Tønnesen T., Horn N. A cytogenetic survey in Menkes disease: implications for the detection of chromosomal rearrangements in X linked disorders. J Med Genet. 1993 Apr;30(4):314–315. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.4.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tønnesen T., Horn N. Prenatal and postnatal diagnosis of Menkes disease, an inherited disorder of copper metabolism. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1989;12 (Suppl 1):207–214. doi: 10.1007/BF01799296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tønnesen T., Petterson A., Kruse T. A., Gerdes A. M., Horn N. Multipoint linkage analysis in Menkes disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 May;50(5):1012–1017. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tümer Z., Chelly J., Tommerup N., Ishikawa-Brush Y., Tønnesen T., Monaco A. P., Horn N. Characterization of a 1.0 Mb YAC contig spanning two chromosome breakpoints related to Menkes disease. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Oct;1(7):483–489. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.7.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tümer Z., Horn N., Tønnesen T., Christodoulou J., Clarke J. T., Sarkar B. Early copper-histidine treatment for Menkes disease. Nat Genet. 1996 Jan;12(1):11–13. doi: 10.1038/ng0196-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tümer Z., Lund C., Tolshave J., Vural B., Tønnesen T., Horn N. Identification of point mutations in 41 unrelated patients affected with Menkes disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1997 Jan;60(1):63–71. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tümer Z., Tommerup N., Tønnesen T., Kreuder J., Craig I. W., Horn N. Mapping of the Menkes locus to Xq13.3 distal to the X-inactivation center by an intrachromosomal insertion of the segment Xq13.3-q21.2. Hum Genet. 1992 Mar;88(6):668–672. doi: 10.1007/BF02265295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tümer Z., Tønnesen T., Böhmann J., Marg W., Horn N. First trimester prenatal diagnosis of Menkes disease by DNA analysis. J Med Genet. 1994 Aug;31(8):615–617. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.8.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tümer Z., Tønnesen T., Horn N. Detection of genetic defects in Menkes disease by direct mutation analysis and its implications in carrier diagnosis. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1994;17(3):267–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00711804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tümer Z., Vural B., Tønnesen T., Chelly J., Monaco A. P., Horn N. Characterization of the exon structure of the Menkes disease gene using vectorette PCR. Genomics. 1995 Apr 10;26(3):437–442. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(95)80160-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilsen B., Andersen J. P., Clarke D. M., MacLennan D. H. Functional consequences of proline mutations in the cytoplasmic and transmembrane sectors of the Ca2(+)-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21024–21030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vulpe C. D., Packman S. Cellular copper transport. Annu Rev Nutr. 1995;15:293–322. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.15.070195.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vulpe C., Levinson B., Whitney S., Packman S., Gitschier J. Isolation of a candidate gene for Menkes disease and evidence that it encodes a copper-transporting ATPase. Nat Genet. 1993 Jan;3(1):7–13. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westman J. A., Richardson D. C., Rennert O. M., Morrow G., 3rd Atypical Menkes steely hair disease. Am J Med Genet. 1988 Jul;30(3):853–858. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieacker P., Horn N., Pearson P., Wienker T. F., McKay E., Ropers H. H. Menkes kinky hair disease: a search for closely linked restriction fragment length polymorphism. Hum Genet. 1983;64(2):139–142. doi: 10.1007/BF00327110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Atkin C. L., Frens D. B., Bray P. F. Menkes' Kinky hair syndrome: studies of copper metabolism and long term copper therapy. Pediatr Res. 1977 Jul;11(7):823–826. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197707000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Forbes J. R., Chen H. S., Cox D. W. The LEC rat has a deletion in the copper transporting ATPase gene homologous to the Wilson disease gene. Nat Genet. 1994 Aug;7(4):541–545. doi: 10.1038/ng0894-541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi Y., Heiny M. E., Gitlin J. D. Isolation and characterization of a human liver cDNA as a candidate gene for Wilson disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Nov 30;197(1):271–277. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. M., Lund T., Niebuhr E., Nørby S., Schwartz M., Shen L. Exclusion mapping of 12 X-linked disease loci and 10 DNA probes from the long arm of the X-chromosome. Clin Genet. 1990 Aug;38(2):94–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1990.tb03555.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarze J. C., Martin P., Muñoz S. J., Friedman L. S. Wilson's disease: current status. Am J Med. 1992 Jun;92(6):643–654. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(92)90783-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]