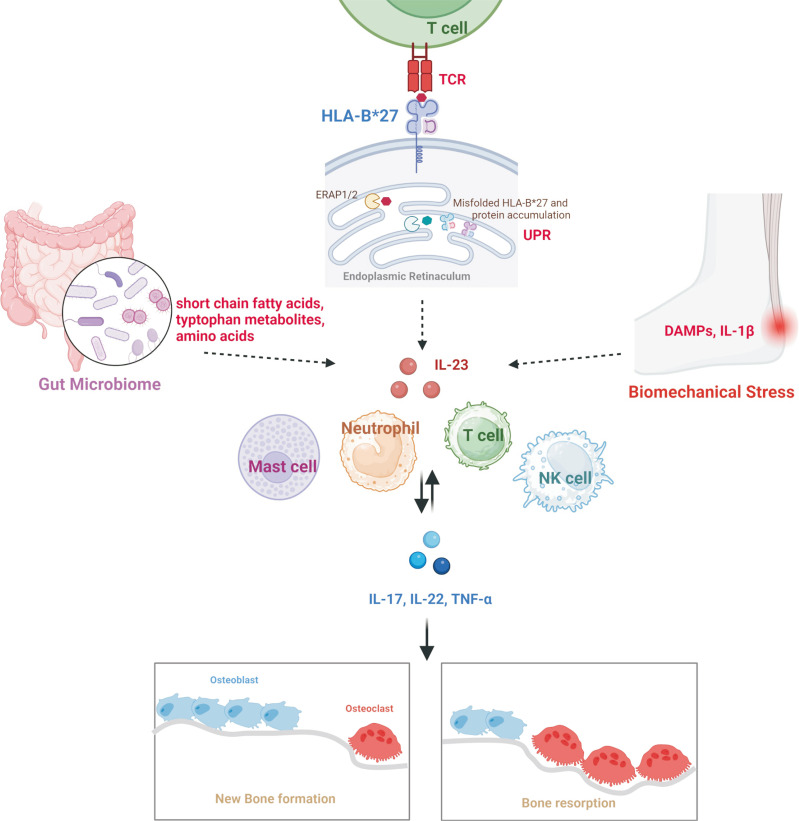
Fig. 1.
Pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis. Gut microbiome produces short-chain fatty acids, tryptophan metabolites, and amino acids. Also, Paneth cells are source of IL-23 in the terminal ileum. HLA-B*27 provides arthritogenic peptide to TCR, and misfolded HLA-B*27 and accumulated protein induce UPR resulting in production of IL-23. Mechanical stress in enthesis induce DAMPs and IL-1β. As a result, produced IL-23 plays a pivotal role in initiating ankylosing spondylitis. Immune cells are involved to progress the disease by inducing IL-17, IL-22, and TNF-α. Bone remodeling is activated, as a result, new bone formation and bone resorption are promoted through cytokines. TCR: T-cell receptor, UPR: unfolded protein response, DAMPs: danger-associated molecular pattern, IL: interleukin, TNF: tumor necrosis factor, NK: natural killer, ERAP: endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidases.