Figure 1:
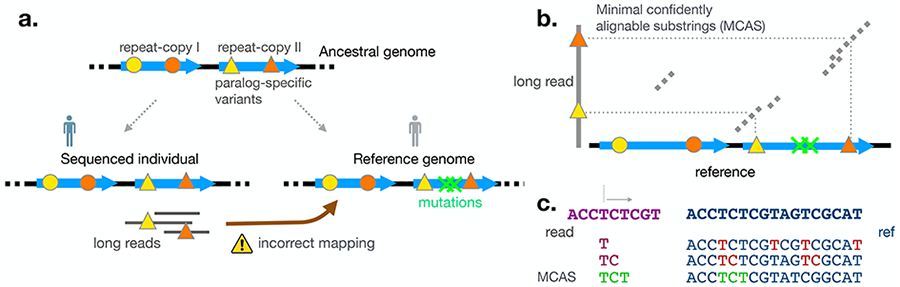
a. Illustration of allelic bias in near-identical genomic repeats. Paralog-specific variants (PSVs), indicated using colored dot and triangle markers, denote variation between two repeat copies in an ancestral human genome . Mutations in the reference sequence are indicated using ‘x’ markers. Long reads can be mapped to an incorrect repeat copy if the best mapping is decided by pairwise sequence alignment score. b. MCAS alignments map to correct loci on the reference. An MCAS is a carefully selected substring of a read. By excluding non-reference alleles, this approach reduces allelic bias. c. A different example is used to illustrate MCAS computation starting from a particular position in a read. To compute MCAS starting from a particular position in a read, we look for the shortest substring that can be uniquely mapped to a reference. Uniqueness of an alignment is determined by using its mapping quality score.
