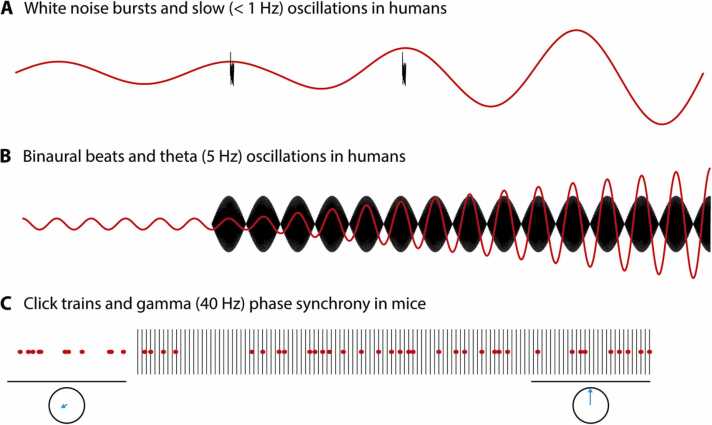
Fig. 5.
Auditory entrainment of hippocampal rhythms (see Section 18 of main text for related behavioral outcomes). (A) Suitably timed white noise bursts (black) boost widespread cortical slow (< 1 Hz) oscillations (red), which propagate to hippocampus and synchronize sharp-wave ripples (not shown) in humans (Ngo et al., 2013). (B) Dichotically presented pure tones separated in frequency by 5 Hz generate binaural beats (black) and boost hippocampal theta oscillations (red) in humans (Derner et al., 2018). (C) 40 Hz click trains (black) affect firing of hippocampal CA1 units (red dots), increasing phase synchrony (blue arrows) at the same (gamma) frequency in mice (Martorell et al., 2019).