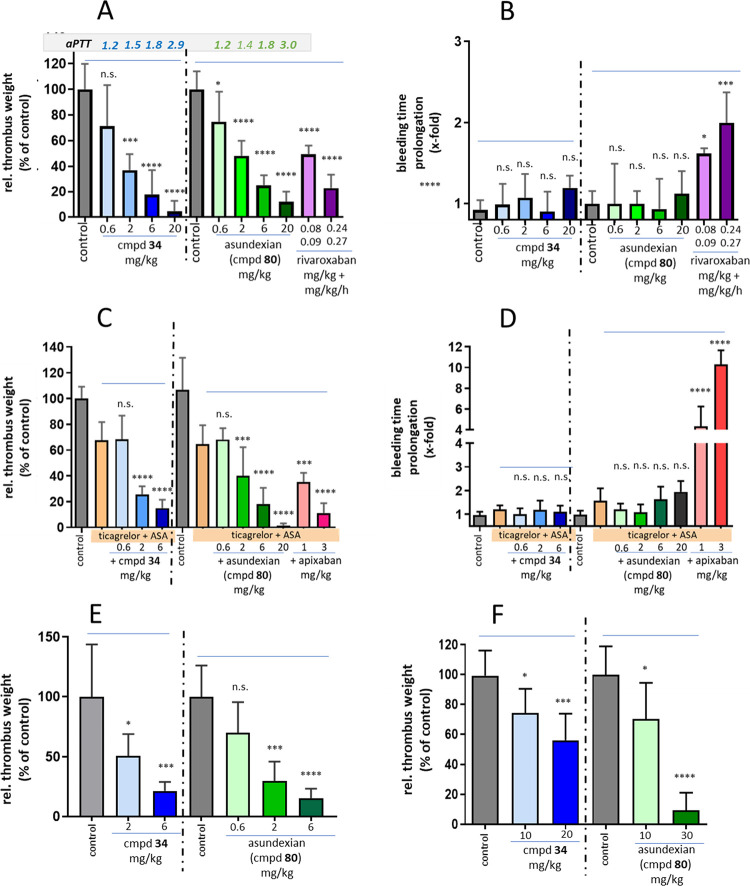
Figure 8.
Antithrombotic effects and impact on hemostasis of compound 34 and asundexian (80) in vivo in rabbit models: (A) dose-dependent thrombus weight reduction after intravenously administered 34 (blue), asundexian (green), and rivaroxaban (magenta) vs control (gray) following FeCl2-induced damage to the carotid artery (arterial thrombosis model) with aPTT prolongation factors given for each dose group, and (B) simultaneously determined impact on bleeding time prolongation after a defined ear incision; (C and D) antithrombotic effects and impact on bleeding time prolongation compared to apixaban (red bars) in the models described in (A) and (B), with the additional presence of aspirin (ASA) and ticagrelor; (E) dose-dependent thrombus weight reduction following FeCl2-induced damage to the jugular vein (venous thrombosis model); (F) dose-dependent impact of orally administered compound 34 and asundexian on the thrombus weight compared to control in the model as described in (A); n = 4–8, mean + SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.