Figure 1.
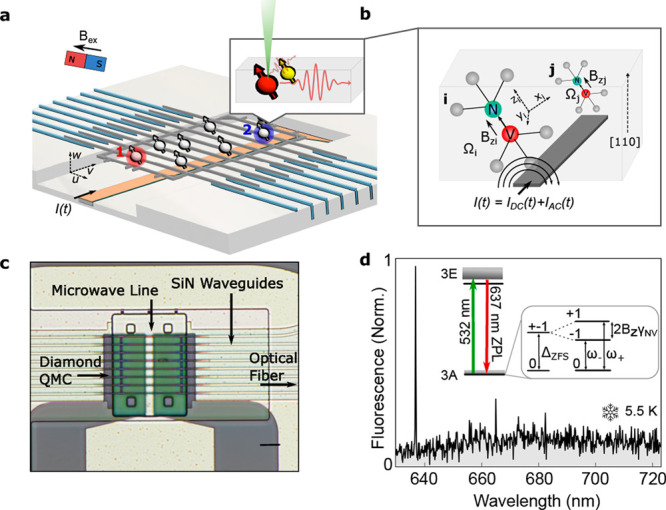
(a) Device structure showing spins in a QMC heterogeneously integrated into a PIC. A free-space laser excites NV centers at a particular location in the diamond waveguide, while NV fluorescence couples to the diamond waveguide mode. In the diamond sample used here, multiple NVs were present at each excitation spot. (b) A current I(t) supplied through the microwave line is used to manipulate NV spin qubits in the QMC. (c) Optical microscope image of the PIC showing an integrated wire for the delivery of microwaves below the diamond QMC. The scale bar is 6 μm. (d) Low-temperature photoluminescence (PL) spectrum of NV centers in the QMC. The inset shows the energy level diagram for NV centers subject to magnetic field Bz.
