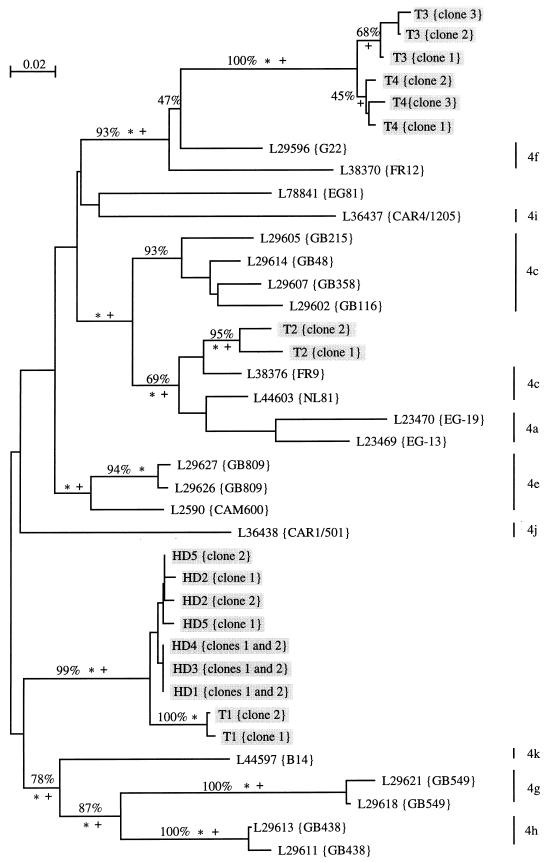
FIG. 2.
Unrooted phylogenetic tree of 38 genotype 4 hepatitis C virus isolates derived from analysis of a partial NS5b sequence (nucleotides 7975 to 8196) retrieved from the EBI databank or by using the Entrez software from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (about 600 sequences). Sequences were aligned manually, and preliminary phylogenetic analyses were used to identify a subset of 120 sequences representative of each monophyletic taxon. More detailed analyses were restricted thereafter to type 4 sequences. The topology was obtained by a maximum-likelihood method (asterisks indicate branches at a P value of <0.01]. Monophyletic taxons also retrieved in the most parsimonious tree are indicated by plus signs. Percentages show branches identified by bootstrap resampling (500 replicates) by using neighbor-joining analysis (13). Trees were drawn with the njplot program for the Macintosh computer (M. Gouy, CNRS URA 243, Université Claude Bernard, Lyon, France). Subtypes of sequences retrieved from data banks were obtained from the persons who deposited the sequences (16, 17). Sequences of viruses from our patients (HD) and from four unrelated controls from the same administrative region (T) are shaded.