Figure 3. Cysteine residues in the p53 DNA-binding domain involved in mutant p53 reactivation.
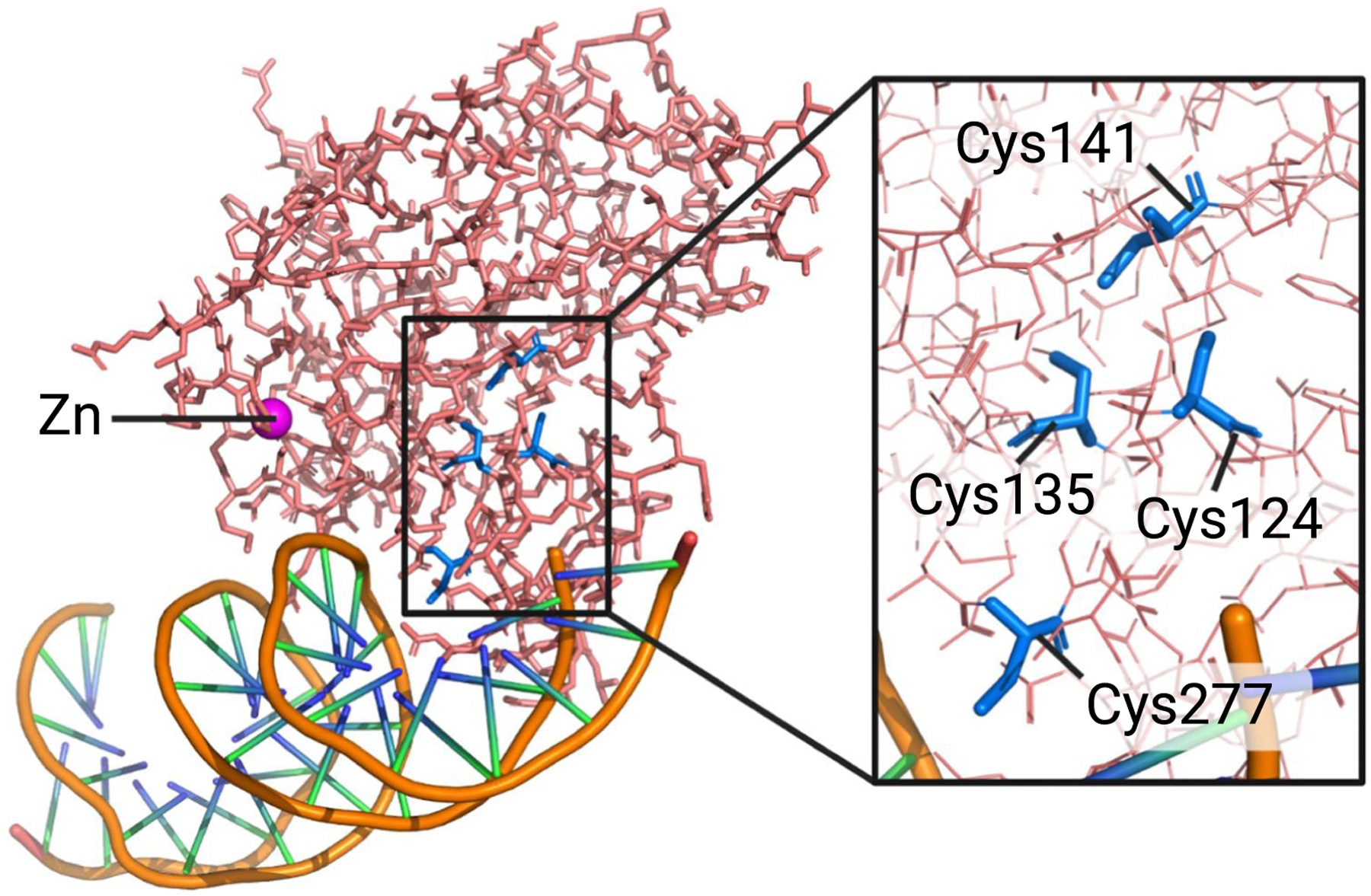
The p53 DNA binding domain bound to DNA (PDB ID: 1TSR) with four cysteine residues involved in p53 reactivation. Cys124 and Cys277 have been linked to PRIMA-1/APR-246-mediated reactivation of p53 mutants [71,72]. Cys124, Cys135, and Cys141 coordinate antimony and arsenic as part of the corrector drug mode of action for antimonials and arsenic trioxide (ATO), respectively [3,4]. Note that arsenic covalently binds to these cysteines, whereas antimony interacts noncovalently. Figure was created in PyMOL.
